Data Sources
A data source describes a JNDI or JDBC connection pool to an SQL database. An FNZ Studio Data Source can be defined as a JDBC Data Source or a JNDI Data Source.
In the FNZ Studio Composition, the Data Source definition tool is located at Data & Integration > Data > Data Sources.
There can be more than one Data Source pointing to the same database, but the name of a Data Source must be unique.
The Data Source overview lists all Data Sources with their state, name and description:
-
An active Data Source has a green state icon. This indicates that the Data Source is available for work.
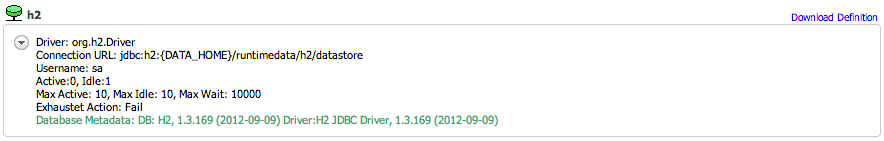
-
An inactive Data Source has a red state icon. This indicates that the targeted database is not accessible, either because of configuration errors or network errors.
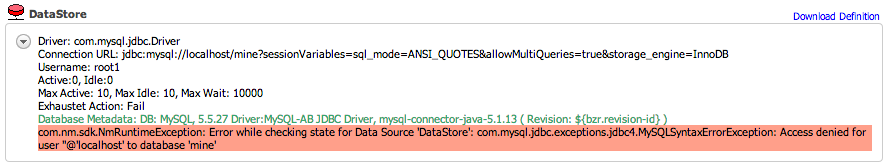
If a Data Source is inactive, a description of the reason for its inactivity is provided at the bottom of the description field.
Creating a Data Source
Expand the menu in the header of the Data Source tool, which provides options to add a JNDI or JDBC Data Source. Alternatively, you can upload a definition, see Examples of JDBC Data Source Definitions and Example of a JNDI Data Source Definition for details.Note: When editing an existing Data Source, consider that a new Connection Pool is created after saving of the configuration. If there are active connections at that time, they are not closed automatically. In that circumstance, a message is reported to the user with the number of active connections.
JDBC Data Source
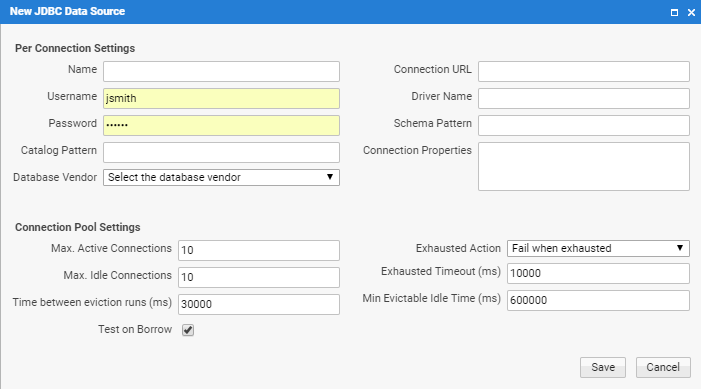
Per Connection Settings
- Name - The name of the Data Source. The name must be unique.
- Connection URL - A driver-specific JDBC connection url.
For example the url
jdbc:mysql://localhost/dataconnects to the database data on the localhost using MySQL. - Username - The name of the user that is connecting to the database.
- Password - The password of the user.
- Driver name - The database-vendor-specific, fully qualified class name of the JDBC driver for the respective database. For example
com.mysql.jdbc.Driveris used for MySQL. Drivers are usually installed in an application-server-specific folder which is part of the classpath. - Schema Pattern - The schema filter used for filtering in the details screen. For most databases, this does not need to be set. If the screen for the context menu option Info takes a long time to load, then specifying this option can help.
- Catalog Pattern - The catalog filter used for filtering in the details screen. For most databases, this does not need this to be set. If the screen for the context menu option Info takes a long time to load, then specifying this option can help.
- Connection Properties - We recommend configuring JDBC Data Sources with a connection timeout to prevent database connection problems from negatively influencing the performance of FNZ Studio.
- 10 seconds timeout for Oracle database:
oracle.net.CONNECT_TIMEOUT=10000oracle.jdbc.ReadTimeout=30000 - 10 seconds timeout for MSSQL database:
loginTimeout=10 - 10 seconds timeout for MYSQL database:
connectTimeout=10000socketTimeout=10000
- 10 seconds timeout for Oracle database:
- Database Vendor - Sets the database vendor. We recommend setting this field, as FNZ Studio uses it to determine the correct SQL dialect to use when generating SQL queries. Selecting Other enables you to specify a custom state script in the State Script field. This script is executed to validate the connection to the database.
Connection Pool Settings
- Maximum Active Connections - The maximum number of active connections in the pool. If this number is reached, the Exhausted Action is executed.
- Exhausted Action - Available options are:
- Fail when exhausted - An exception is thrown if the pool is still exhausted after waiting for a connection.
- Block when exhausted - Waits indefinitely for a connection (neglects the
Maximum Wait Timeproperty). - Grow when exhausted - Allows the pool to grow infinitely (neglects the
Max Active Connectionsproperty).
- Maximum Idle Connections - The maximum numbers of idle connections. If this number is reached, the extra connections in idle state are closed.
- Exhausted Timeout (ms) - The maximum time to wait for retrieving a new connection when the pool is exhausted. Time between eviction runs (ms) - Sets the number of milliseconds to sleep between runs of the idle object evictor thread. This thread cleans idle connections that are eligible for eviction.
- Min Evictable Idle Time (ms)- Sets the minimum amount of time an object may sit idle in the pool before it is eligible for eviction by the idle object evictor.
- Test on Borrow - Specifies whether a connection is validated before it is borrowed from the pool. If the connection fails to validate, it is dropped from the pool, and FNZ Studio attempts to borrow another. The validation is performed by executing a simple vendor-specific query (e.g. SELECT 1).
JNDI Data Source
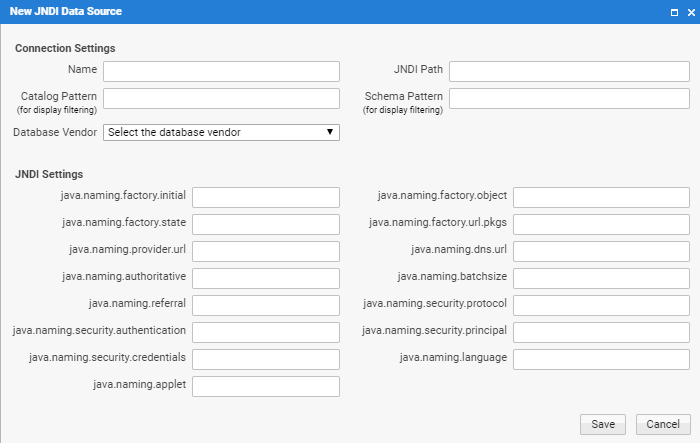
The following options are available:
- Name - The name of the Data Source. This name will be used in the solution to reference the Data Source.
- JNDI Path - The JNDI path the the Data Source as defined in the application server's directory service.
For example:
java:/com/end/jdbc/oracleDB - Catalog Pattern - The catalog pattern used for accessing the database. This may be empty for many databases. Enter a value only if required by the database driver.
- Schema Pattern - The schema pattern used for accessing the database. This should be provided for Oracle databases to enhance performance.
- Database Vendor - Sets the database vendor. We recommend setting this field, as FNZ Studio uses it to determine the correct SQL dialect to use when generating SQL queries.
- JNDI Settings - Specify the JNDI environment attributes as required by your directory service.
Examples of JDBC Data Source Definitions
This section provides examples of JDBC data source definitions.
Instead of using the JDBC Data Source dialog described in an earlier section, you can upload a definition to create a new data source. Expand the menu in the header of the Data Source tool and select Upload Definition.
MySQL Example
Name: mysql
Connection Url: jdbc:mysql://mysql.numcom.local/mydb
Optional Url Parameters: ?sessionVariables=sql_mode=ANSI_QUOTES&allowMultiQueries=true
Username: root
Password:
Drivername: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
If InnoDB is required because support for transactions is mandatory, append the session variable "storage_engine=InnoDB" to the connection url. A complete connection url would look like this:
jdbc:mysql://mysql.numcom.local/mydb?sessionVariables=sql_mode=ANSI_QUOTES&allowMultiQueries=true&storage_engine=InnoDB
Force UTF-8 encoding session parameters:
useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=UTF-8
Example connection url with UTF-8 character set:
jdbc:mysql://localhost/runtimedata?sessionVariables=sql_mode=ANSI_QUOTES&allowMultiQueries=true&storage_engine=InnoDB&useUnicode=yes&characterEncoding=UTF-8
Oracle Example
Name: oracle
Connection Url: jdbc:oracle:thin:@//oracle.numcom.local:1521/SID
Username: root
Password:
Drivername: oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
Sybase Example
Name: sybase
Connection Url: jdbc:jtds:sybase://sybase.numcom.local:5000/mydatabase
Username: sa
Password:
Drivername: net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
See jTDS FAQs
Connection with 8 seconds login timeout and 180 seconds overall query timeout:
jdbc:jtds:sybase://sybase.numcom.local:5000/msus;loginTimeout=8;socketTimeout=180
MS SQL Example
Name: mssql
Connection Url: jdbc:jtds:sqlserver://mssql.numcom.local:1433;databaseName=mydb
Username: root
Password:
Drivername: net.sourceforge.jtds.jdbc.Driver
Name: mssql
Connection Url: jdbc:sqlserver://mssql.numcom.local:1433;databaseName=mydb
Username: root
Password:
Drivername: com.microsoft.sqlserver.jdbc.SQLServerDriver
H2 Example
Name: h2
Connection Url: jdbc:h2:{DATA_HOME}/local/h2/database
Username: sa
Password:
Drivername: org.h2.Driver
(the server is automatically started, datafiles are in the folder /local/h2)
HSQLDB Example
Name: hsqldb
Connection Url: jdbc:hsqldb:hsql://hsqldb.numcom.local:9001/datastore
Username: sa
Password:
Drivername: org.hsqldb.jdbcDriver
Create New Instance: Yes
2.7 PostgreSQL Example
Name: PostgreSQL
Connection Url: jdbc:postgresql://server.domain.com:5432/postgres
Username: test
Password:
Drivername: org.postgresql.Driver
Example of a JNDI Data Source Definition
This section provides an example of a JNDI data source definition.
Instead of using the JNDI Data Source dialog described in a previous section, you can upload a definition to create a new data source. Expand the menu in the header of the Data Source tool and select Upload Definition.
jdbc/oracleDBis an example of the name of the JNDI resource being defined.
FNZ Studio Configuration:
Name: oracle
JNDI Path: java:/comp/env/jdbc/oracleDB
Catalog Pattern:
Database Vendor: Oracle
Schema Pattern: TIGER
JNDI Settings: none
Password Encryption
You can define a password encryption key for increased security. Expand the menu in the header of the Data Source tool and select Set Password Encryption Key. If a master password is defined on your system, it must be entered to set a password encryption key, otherwise leave the field empty. You can remove the password encryption key at the same location.