Troubleshooting Console
Introduction
The Troubleshooting Console was designed to support troubleshoot various FNZ Studio integrations:
- OIDC integration
- Calls to WebAPIs
- WebServices calls
- MQ Systems
Note the following:
-
Data is collected on each cluster node and stored in memory only for a short period of time (30 minutes by default). This threshold can be changed through configuration property
nm.integration.troubleshooting.cache.max.age.ms(System Configuration > Configuration Properties in FNZ Studio Composition). -
Data is stored in a cache of a fixed length (1000 entries by default). This limit can be changed through configuration property
nm.integration.troubleshooting.cache.max.size.Warning: Larger caches require more memory. Setting the limit too high may cause memory issues.
The Troubleshooting Console page in FNZ Studio Composition (Data & Integration > Integration) displays data from all nodes in a single view with filtering options.
To access this page, the Integration Troubleshooting Console Studio Permission (see Advanced Studio Permissions) must be enabled.

Schemas
Troubleshooting data is split in multiple sections called schemas. Three schemas are implemented:
- HTTP — Collects troubleshooting data in HTTP calls.
- Kafka — (KafkaConnector Extension 2.0.0 or higher must be installed) Collects troubleshooting data on Kafka event streaming.
- OIDC — (OIDCAuth Extension 4.0.0 or higher must be installed) Collects data on OpenID Connect integration calls. Note that this extension is internal (FNZ projects) only. See documentation (internal).
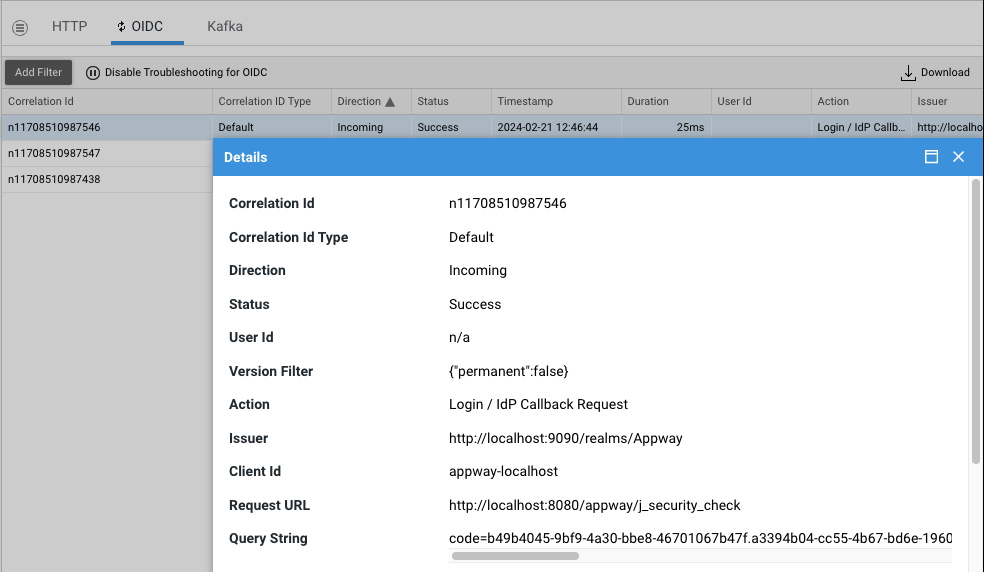
Every schema displays general information in a data table - every item in the data table representing an integration call. For each integration call, more details are shown in a pop-up by double-clicking on the row or by right-clicking the row and the choosing Details.
Activation
Data collection must be activated on demand for every schema, and it is automatically deactivated when FNZ Studio stops/restarts.
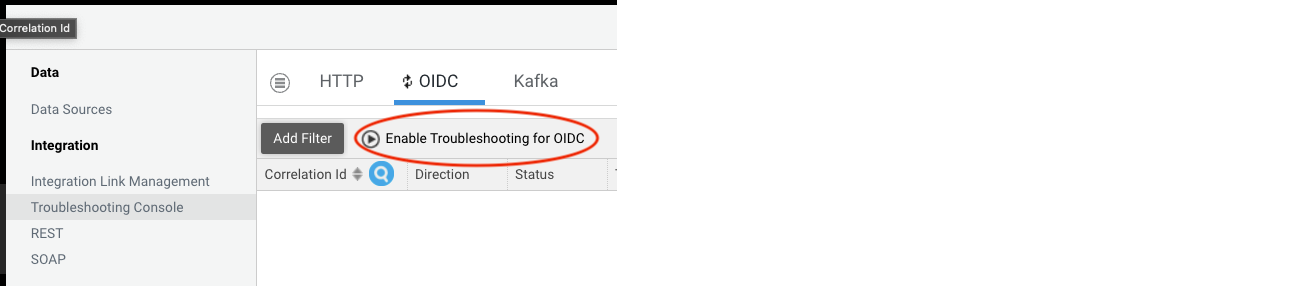
For security reasons, theIntegration Troubleshooting Console (full access) Studio Permission (see Advanced Studio Permissions) is needed to enable or disable schemas. Audit logs are collected every time a schema is activated or deactivated.
Attributes
Default Attributes
For every schema, the following information is shown for each integration call (if available):
CorrelationId: Integration identifier, it can be:- Process Instance: Uses the Process Instance ID (where available).
- Default: Uses a randomly generated ID along with node information.
Direction: Whether the integration is outgoing or incomingStatus: Overall outcome of the integration call (Unknown, Success, Error)Timestamp: Time at which the integration call startedDuration: How long the integration call tookUserId: User who triggered the callException: Error message (if any) regarding a failed integrationVersion filter: Business Object version filter that was used (if available)
Attribute Limits
Every schema enriches the default attributes with others attributes specific to its use case.
These attributes are trimmed if their size exceeds a certain limit. The default limit is 1000000 bytes (~1Mb). This can be configured up to a max of 2147483647 bytes (~2Gb) via the nm.integration.troubleshooting.max.attribute.size configuration property (System Configuration > Configuration Properties in FNZ Studio Composition).
There is a maximum of total data kept in memory for the troubleshooting console at any given time. If the limit is reached, data is rotated, i.e. the oldest entries are removed to create space for latest ones.
Sensitive Data
Known sensitive data collected in attributes is masked for security reasons.
Example: JSESSIONID=C9111986FB91...E498
Collected Data
HTTP Schema
The HTTP schema is provided by the FNZ Studio Core Platform, therefore no additional extension is needed. It helps monitor HTTP traffic to and from FNZ Studio.
The following integration calls are available:
- Incoming: WepAPIs
- Outgoing:
- Calls performed with
HTTPGET()andHTTPPOST()script functions. - SOAP and REST integration calls (WebServices Extension 5.0.0 or higher is needed).
- Calls performed with the SOAPServiceCall() Script Function (WebServices extension v5.0.0 or higher is needed).
- Calls performed with
Attributes
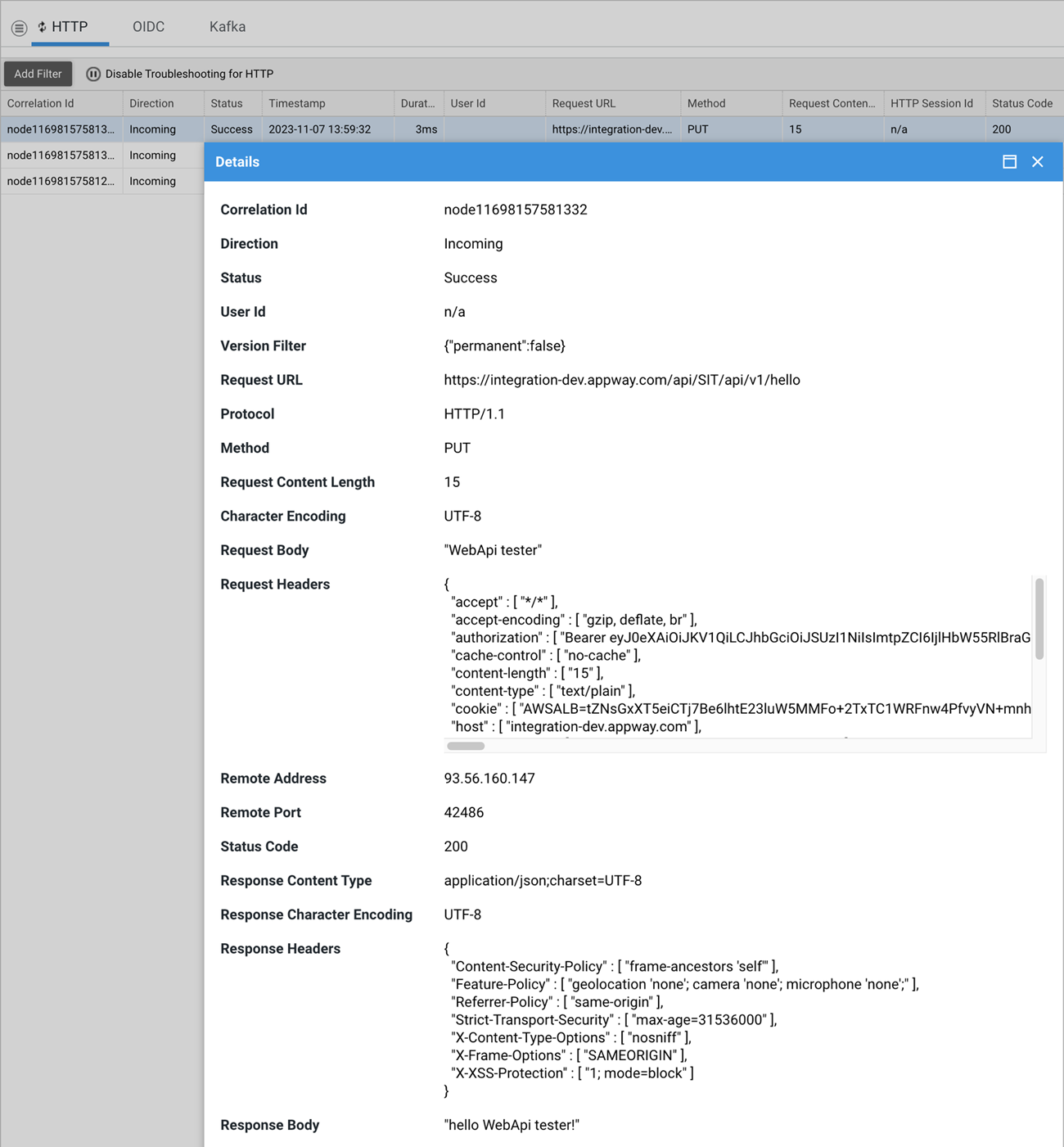
When enabled, the console collects information useful to identify and analyze incoming/outgoing requests and their outcome.
The following attributes are collected:
Request URLQuery StringProtocolMethodRequest Content LengthCharacter EncodingRequest BodyRequest HeadersRequest ParametersHTTP Session IdRemote UserRemote AddressRemote PortAuthentication TypeRequest contextStatus CodeResponse Content TypeResponse Character EncodingResponse HeadersResponse Body
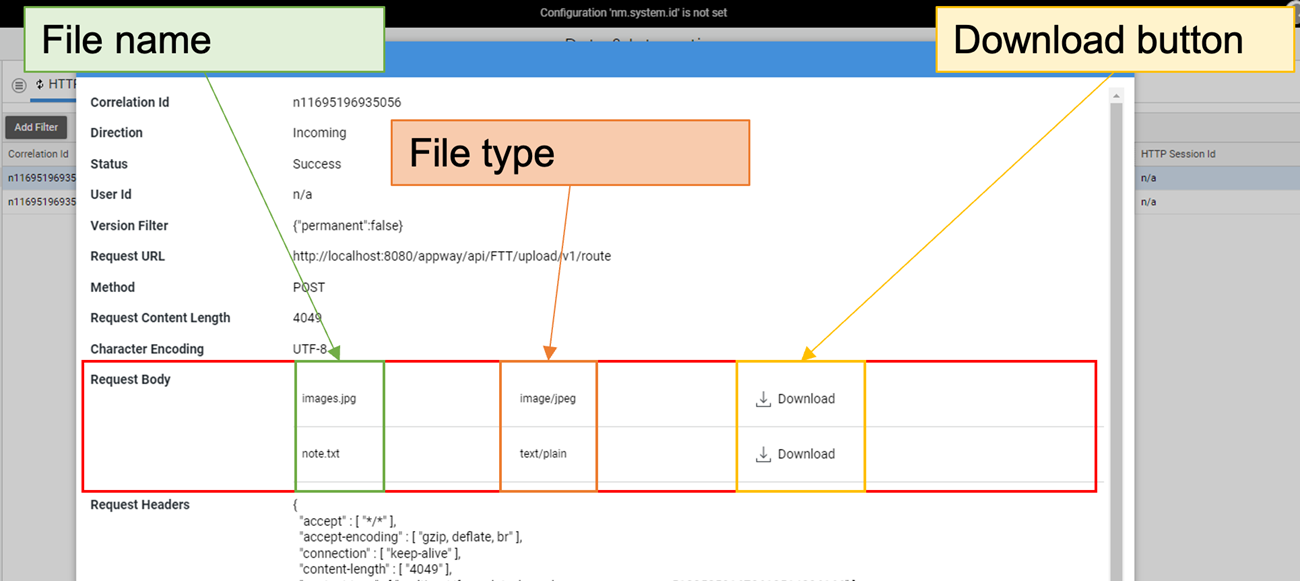
File Support
Requests that contain files are parsed and shown in the Troubleshooting Console as shown below. These files can be downloaded on demand.
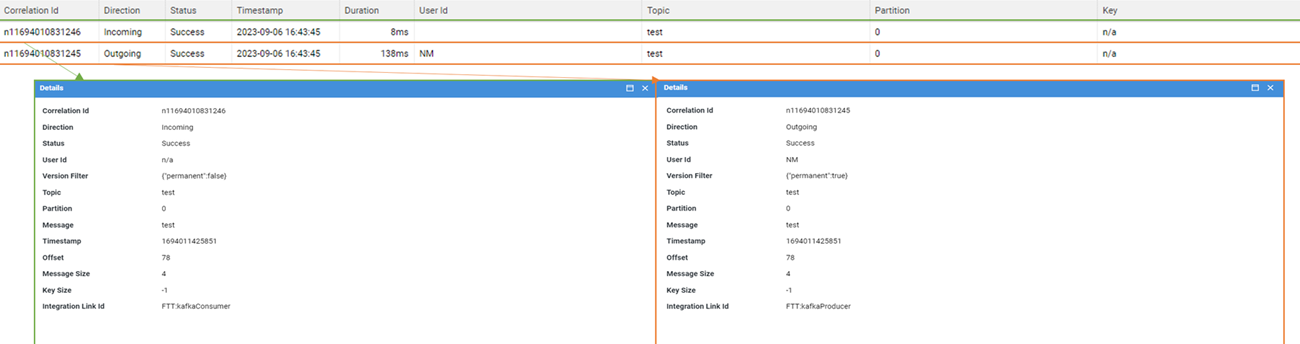
Kafka Schema
Kafka schema exposes all the basic attributes and metadata of the messages.
Attributes
The following attributes are collected:
Message: The event messageKey: The event keyMessage Size: The event message (in bytes)Key Size: (in bytes)Timestamp: Time at which the event was createdHeaders: Event headersIntegration Link Id: Name of the related Integration LinkOffset: Consumer offset*Topic: Where events are organized*Partition: Chunks of a single topic*
OIDC Schema
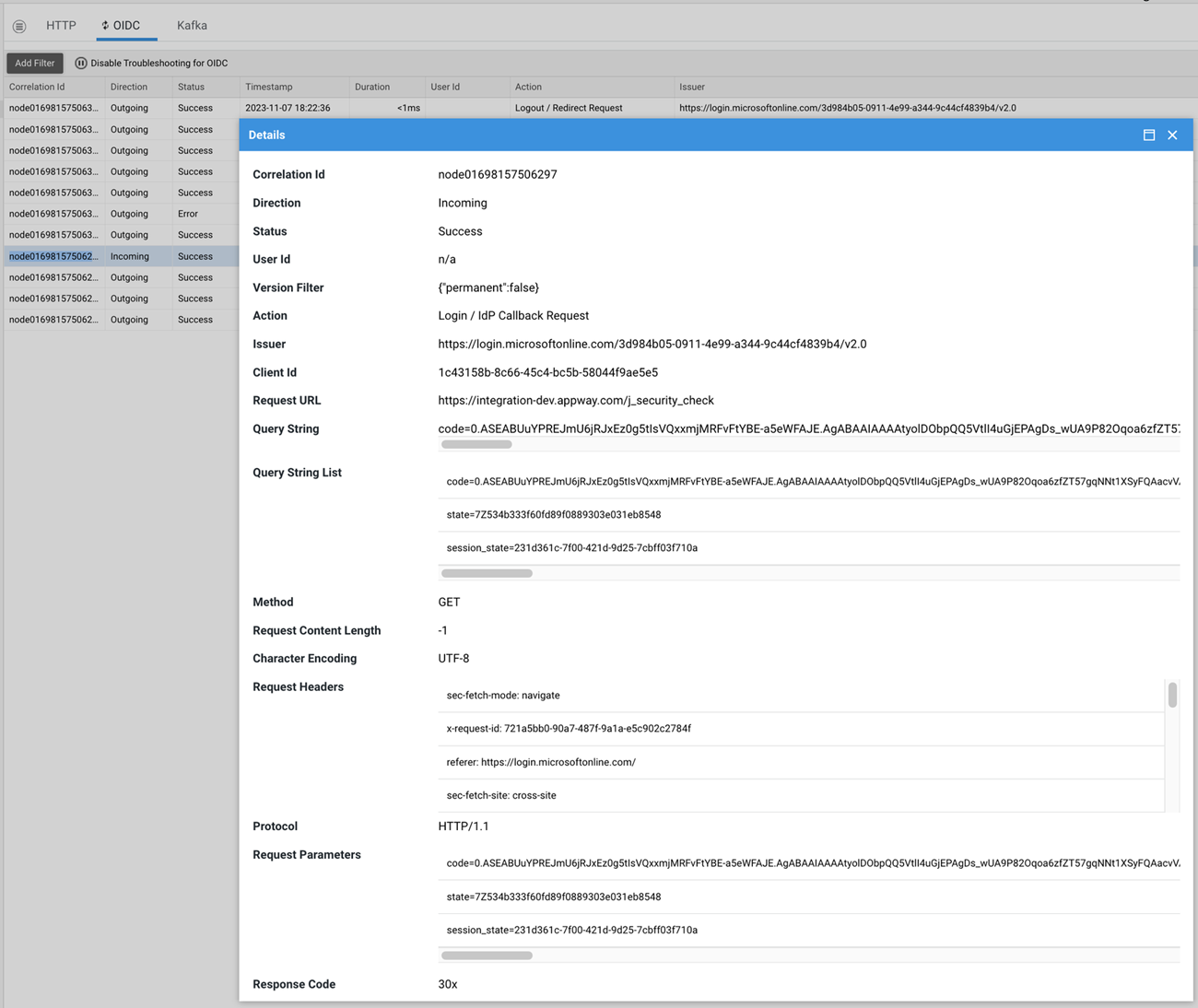
OIDCAuth Extension (v4.0.0 or higher) helps troubleshoot integration calls between FNZ Studio the and registered Identity Providers (IdP), such as Keycloak or Microsoft Azure. Note that this extension is internal (FNZ projects) only. See documentation (internal).
Integration Calls
Currently the Troubleshooting Console supports the following use-cases** :
- Login
- IdP Callback Request: When the IdP redirects the user back to FNZ Studio after authentication.
- Code Exchange Request: When FNZ Studio exchanges authorization code for an access/ID token.
- Logout
- Redirect Request: When the user requests to log out and the request is redirected to the IdP.
- Back-Channel Request: When the IdP requests the user's logout.
- Access
- Client Credential Request: When an access token is requested for a machine-to-machine call.
- Refresh Token Request: When the access token is refreshed.
- Fetch
- Open Id Configuration: When the OpenID Connect configuration is fetched for the configured IdPs.
- Access
- Web Api Request: when a Web API is called with a bearer token. Note: In this case, the information shown in the OIDC schema is limited to the authentication process and more information can be found in the HTTP schema.
Attributes
Similarly to HTTP schema, the information collected help troubleshoot requests between FNZ Studio and the IdP.
IdP-Related Attributes
Action: Integration call it refers toIssuer: IdP's unique identifierClient Id: Client ID configured for the issuer (IdP)Id Token: ID token provided by the IdPAccess Token: Access token provided by the IdPRefresh Token: Refreshes the token provided by the IdPRoles Mapping Warnings(only visible in flows Login / IdP Callback Request and Verification / Web Api Request): Generic attribute that provides different hints based on the request received and system configuration. It is useful for debugging missing roles and system property configurations.Roles Mapping Tracing(only visible in flows Login / IdP Callback Request and Verification / Web Api Request): Attribute that displays the Role received (Role retrieved from the claim), the Role processed from it (Roles after claim mapping), and the Roles that result from the filtering executed by thenm.auth.rolessystem configuration property at login.
HTTP Attributes
Request URLQuery StringQuery String ListMethodRequest Content LengthCharacter EncodingRequest BodyRequest HeadersProtocolRequest ParametersResponse CodeResponse Url RedirectionResponse DateResponse Body
Token Masking
For security reasons, all tokens are masked.
The JWT tokens are masked by stripping the signature part such that the header and payload can still be read and decoded but the tokens cannot be re-used.
Example: Token=eyJhbGciOiAiUlNBLU9BRVAiLCAidHlwIjogIkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiAidXNlciJ9.###SIGNATURE###
Integration Call Diagrams
Login
IdP Callback Request

- A User in FNZ Studio asks to log in trough IdP.
- FNZ Studio redirects the user to the IdP authorization endpoint.
- The IdP redirects the user to FNZ Studio after authentication.
Code Exchange Request

- A User in FNZ Studio asks to log out.
- FNZ Studio forwards the logout request to the IdP.
Logout
Redirect Request

- User in FNZ Studio asks to log out.
- FNZ Studio forwards the logout request to the IdP.
Back Channel Request

If the Back-Channel Logout feature is enabled on the IdP, a logout request from any relying party application will trigger a call to the back channel logout endpoint for every relying party applications.
Access
Web Api Request

- An actor calls a Studio Web API with a bearer token for authentication.
- FNZ Studio validates the token and authenticate the request.
Client Credentials Request

- An access token is requests for a machine-to-machine request.
- The IdP validates the data received and responds with the access token.
Refresh Token

- An access Token is used in FNZ Studio.
- If the token is about to expire, it is refreshed before being used.
Fetch
Open Id Configuration
 FNZ Studio fetches the IdP configuration.
FNZ Studio fetches the IdP configuration.