IntegrationLinkComponents Extension
The IntegrationLinkComponents extension deploys Active MQ JMS Integration Link components which allow FNZ Studio to send and receive text messages to/from an Active MQ JMS broker.
The components can be configured to communicate with JMS queues or JMS topics.
See the Integration Link section for further context.
Broker Definition
FNZ Studio requires access parameters for every Active MQ broker in use. Define brokers using the configuration properties of the extension. Access the properties via Extensions in FNZ Studio Composition. Right-click IntegrationLinkComponents and select Edit Configuration.
Define direct access to Active MQ brokers using the configuration property activemq.brokers. If this method is used, FNZ Studio creates the connection factory used for creating listeners and notifiers.
The alternative configuration property activemq.jndi.connectionFactories can be used to define the location of a preconfigured connection factory on JNDI.
Details on the extension configuration properties follow:
-
activemq.brokers – A semicolon separated list of Active MQ broker definitions. The pattern used for a broker is:
(NAME '|' BROKERURL '|' UID? '|' PW? ';')*- NAME: the internal name of the broker
- BROKERURL: the URL including the port where the broker can be contacted
- UID: optional user ID
- PW: optional password
Example:
amq|tcp://activemq.local:61616|admin|secret; -
activemq.jndi.connectionFactories – A semicolon separated list of JNDI paths to preconfigured connection factories. The pattern used for the broker is:
( NAME '|' JNDI_PATH ';')*- NAME: the internal name of the broker
- JNDI_PATH: JNDI access path to the connection factory
Example:
broker1|java:comp/env/jms/ConnectionFactory1;
Active MQ Listener
The Active MQ Listener Integration Link Active MQ Listener Integration Link component provides listener (receive) access to JMS queues or topics served by an external Active MQ broker.
Select ActiveMQ Listener from the Select a Start Element drop-down box:
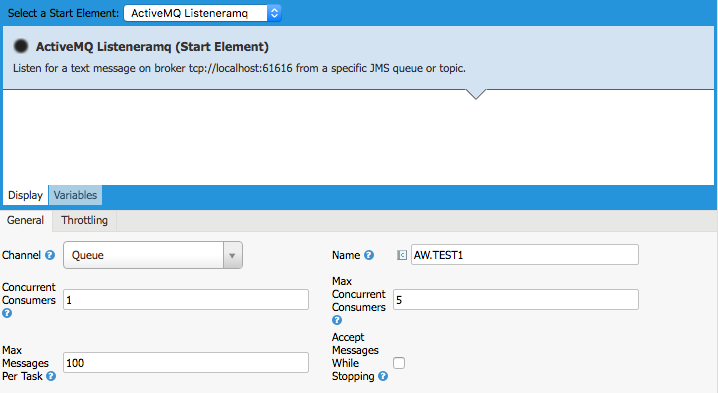
The Active MQ Listener component can be configured via the General and Throttling tabs.
| Field | Description |
| Channel | Defines the used JMS channel: Queue or Topic. |
| Name | Defines the queue or topic name. |
| Concurrent Consumers | Sets the default (minimum) number of concurrent consumers processing incoming messages. This setting is intended for each node. |
| Max Concurrent Consumers | Sets the maximum number of concurrent consumers. This allows the consumer pool to grow if required (dynamic scaling). This setting is intended for each node. |
| Max Messages Per Task | Sets the maximum number of message reception attempts per task (i.e. per concurrent consumer). Use this option to control how fast the number of consumers decreases when the workload is low and a range for concurrent users is defined (“Concurrent Consumers” – “Max Concurrent Consumers”). The higher the value for “Max Messages Per Task”, the longer idle consumers are kept. Default value = 100. Set “-1” for unlimited. |
| Accept Messages While Stopping | Specifies that the consumer accepts messages while it is stopping. Enable this option, if you start and stop JMS routes at runtime, while there are still messages in the queue. If this option is disabled, and you stop the JMS route, then messages can be rejected, and the JMS broker has to attempt redeliveries, which can be rejected again. Eventually, the message could be moved to a dead letter queue on the JMS broker. To avoid this scenario, we recommend to enable this option. |
On the Throttling tab, you can define an inflight throttling policy that sets an upper limit on the concurrent number of messages that the component can process. This feature allows to dynamically throttle routes at runtime based on the current number of inflight exchanges.
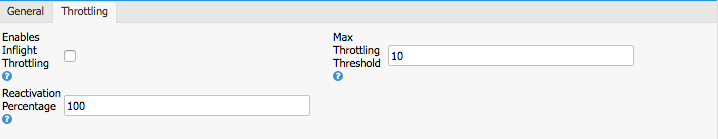
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enables Inflight Throttling |
Enables inflight throttling for the listener. |
|
Max Throttling Threshold |
|Sets the maximum value of inflight exchanges. When this value is reached, throttling starts to suspend the route. (Also consider the value “Max Messages per Task” on the “General” tab). Note: This value must be lower than the “Max Concurrent Consumers” defined on the General tab. If not, throttling does not have any effect. |
| Reactivation Percentage | Defines a percentage specifying when throttling should resume the route after it has been suspended. Example: “Max Throttling Threshold” is 20 and “Reactivation Percentage” is 10. The route is resumed when the number of inflight messages is <= 2. |
Active MQ Notifier
The Active MQ Notifier Integration Link component provides notification (send) access to JMS queues or topics served by an external Active MQ broker.
Drag the Active MQ Notifier Integration Link component into an Integration Link from the End Component element library.
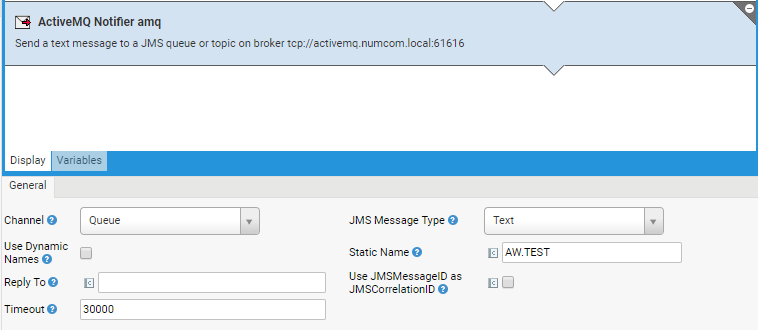
The Active MQ Notifier component can be configured via the General tab.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Channel | Specifies the used JMS channel: Queue or Topic. |
| JMS Message Type | Specifies the JMS Message Type used when sending a message to a Queue or Topic: Text or Bytes. |
| Use Dynamic Names | Allows you to define a script expression which dynamically returns the names of queues or topics to be notified.nWhen this option is enabled, the name of the channel is evaluated on a per message basis. |
| Dynamic Names (available if Use Dynamic Names is enabled) | Dynamically defines an indexed collection of queue or topic names. The indexed collection must contain the final names of queues or topics to which the exchange should be forwarded to. |
| Static Name (available if Use Dynamic Names is disabled) | Sets a static name for the queue or topic to be notified. A single value. |
| Reply To | Name of the queue to reply to (used only if the value is not empty). |
| Use JMSMessageID as JMSCorrelationID | Specifies that the JMSMessageID is used as the JMSCorrelationID for messages. |
| Timeout | Defines the timeout in milliseconds when waiting for a reply if the Request-Reply message exchange pattern is used. |
Terminology
- An “inflight exchange” is a message that has been de-queued from ActiveMQ and is currently being processed by a thread. This thread is also called a consumer.
- “Concurrent consumers” (per node). A consumer is an executing thread that listens and consumes messages from a predefined queue. If the number of concurrent consumers is 3, then the maximum number of inflight exchange messages is also 3.