ProcessAuditTrail Extension
Introduction
The ProcessAuditTrail extension tracks a running process' information flow. It logs all actions about its state, and stores them into a relational database. Other data, such as instance or token attributes and custom messages, can be logged as well. Use this stored information for your own purposes, such as keeping an audit trail (i.e. what happened when and where), or conducting business intelligence (e.g. the time it usually takes for process XYZ to complete for customers in Germany).
This document is intended for people who have to install and configure this extension and/or prepare the database. It is also suitable for business users who want to see what data can be collected or what can be further analyzed.
How It Works
Consider this example:
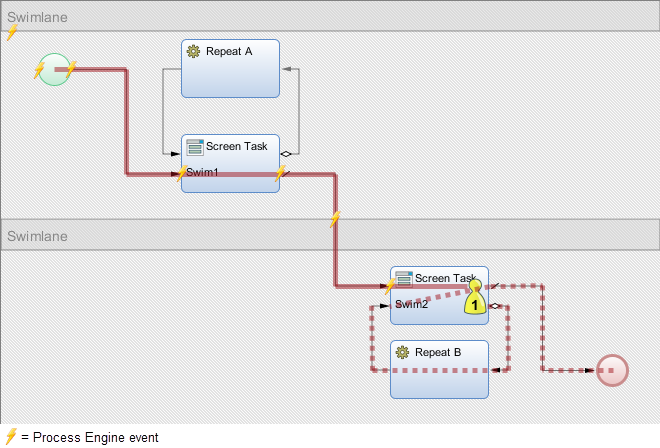
Figure 1: Example process
Figure 1 shows an example process. A particular process instance flow is represented by the solid red line and ends following the dashed line. The process instance triggered many events in the Appway process engine. The ProcessAuditTrail extension collects these events, transforms them into log entries and stores them into the database. The level of detail of collected and stored data is configurable (see Data Collection Properties).
We illustrate how the ProcessAuditTrail extension collects and stores information based on the flow marked by the dashed line in Figure 1. The user is on the "Swim 2” Screen Task and clicks the "Repeat" button. The process instance proceeds to the "Repeat B" Script and then gets back to the Screen "Swim 2".
Figure 2 illustrates the processing of a particular user action. The user clicks on the repeat button, which triggers an HTTP request sent to Appway core, which in turn, invokes the process engine.
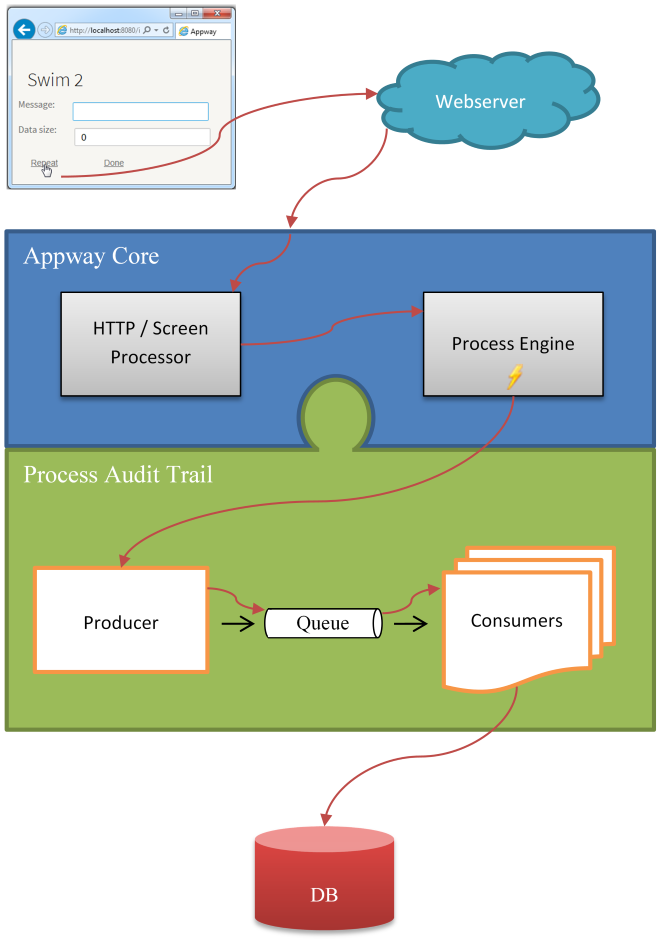
Figure 2: Example process details
While the Process Engine does its work, multiple events are generated. These events are collected by the ProcessAuditTrail extension and then converted into commands by the Producer component. Commands are data structures which describe the raised events. The Producer adds the commands to a queue, and the commands are later consumed asynchronously. The consumer threads of the Consumer component translate the commands into database statements and execute them. The collected data is available in technical database tables but also as human-readable log entries (see Figure 15: Entity Relationship Diagram).
With our example dashed process flow and the extension's default configuration, the following commands are generated:
- Token End End event of Screen "Swim 2". It updates the Screen's token in database table "token" and sets its state to completed.
- Audit Trail Log A human-readable log message which says that the Screen is now complete. It inserts a new message record into the database table "audit_log".
- Token Start Start event of Script "Repeat B". It inserts the Script's token into database table "token" with state= started.
- Audit Trail Log A human-readable log message which states that the Script has started. It inserts a new message record into the database table "audit_log".
- Token End End event of Script "Repeat B". It updates the Script's token status in database table "token" to completed.
- Audit Trail Log A human-readable log message which says that the Script is now complete. It inserts a new message record into the database table "audit_log".
- Token Start Start event of Screen "Swim 2". It inserts the Screen's token into database table "token" and sets its status to started.
- Audit Trail Log A human-readable log message which says that the Screen has now started. It inserts a new message record into the database table "audit_log".
- Token User User assigned event for Screen "Swim 2". It inserts the current user into the database table "token_user".
Collecting Events
The extension attaches to the Process Listener, which is an infrastructure that listens to events generated by the Appway process engine. These events are prepared as commands and stored into a queue. They contain a human-readable text message which is defined in various Labels. As such, the process is detached and continues working while the data is consumed from the queue and stored in the database (producer/consumer).
You can customize the Labels used with any text and translation. A list of all Labels used is presented later in this document.
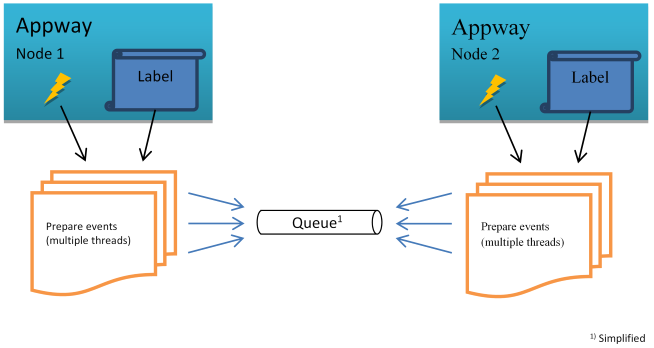
Figure 3: Collecting events
It doesn't matter on which node events for a certain process instance are generated. Since the queue is distributed, the changes are visible on all nodes.
Storing Events
A consumer thread takes a command from another thread in the queue and stores it into the database. The number of consumers is configurable ("processaudittrail.async.logger.count").
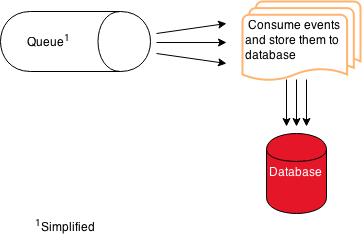
Figure 4: Storing commands
There is always a designated node responsible for storing all commands of a certain process instance ID.
Implementation Detail
To be able to register distributed maps, this extension runs in Appway as a plug-in.
The Queue
The queue, as depicted earlier, is only a simplification. During implementation, it uses multiple distributed maps to achieve the queue behavior.
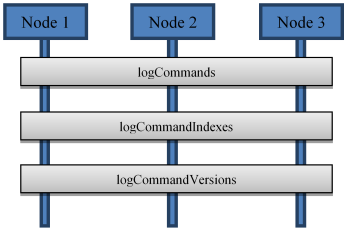
Figure 5: Distributed maps used
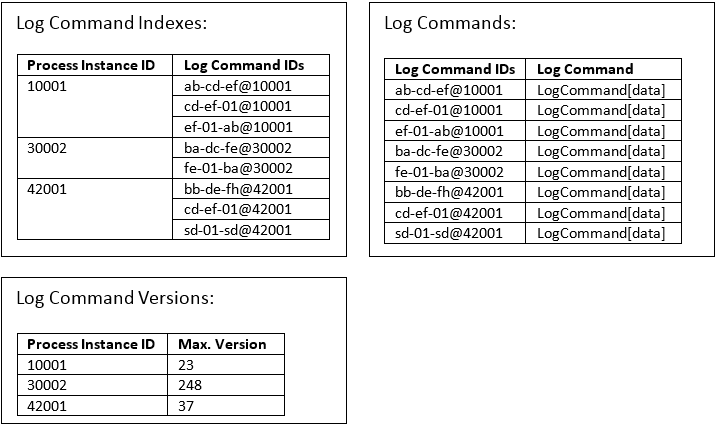
Figure 6: Example map entries
Three distributed maps are used:
- logCommandIndexes Contains administration information for commands per process instance. Simply put, it maintains the proper order of the commands.
- logCommands Contains each command. When consumed, the command results in one or more database insert, update or delete.
- logCommandVersions Contains version information per process instance. Each database table has the process instance ID and version as primary keys. The version is maintained and incremented after each event.
Collecting
When Appway processes an HTTP request or triggers an update on a process instance, it happens in the context of a certain Java thread. While this thread is active, all Process Engine events are collected by this extension in a data structure that is visible only to this thread (so-called thread-local variables). Before the thread ends, the extension hooks in, stores the thread-local data into its distributed maps, and does a cleanup. Afterwards, the regular put to the Appway core distributed maps takes place.
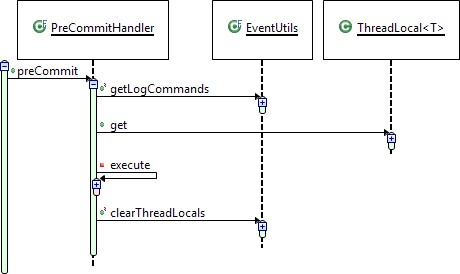
Figure 7: Collecting details: Overview
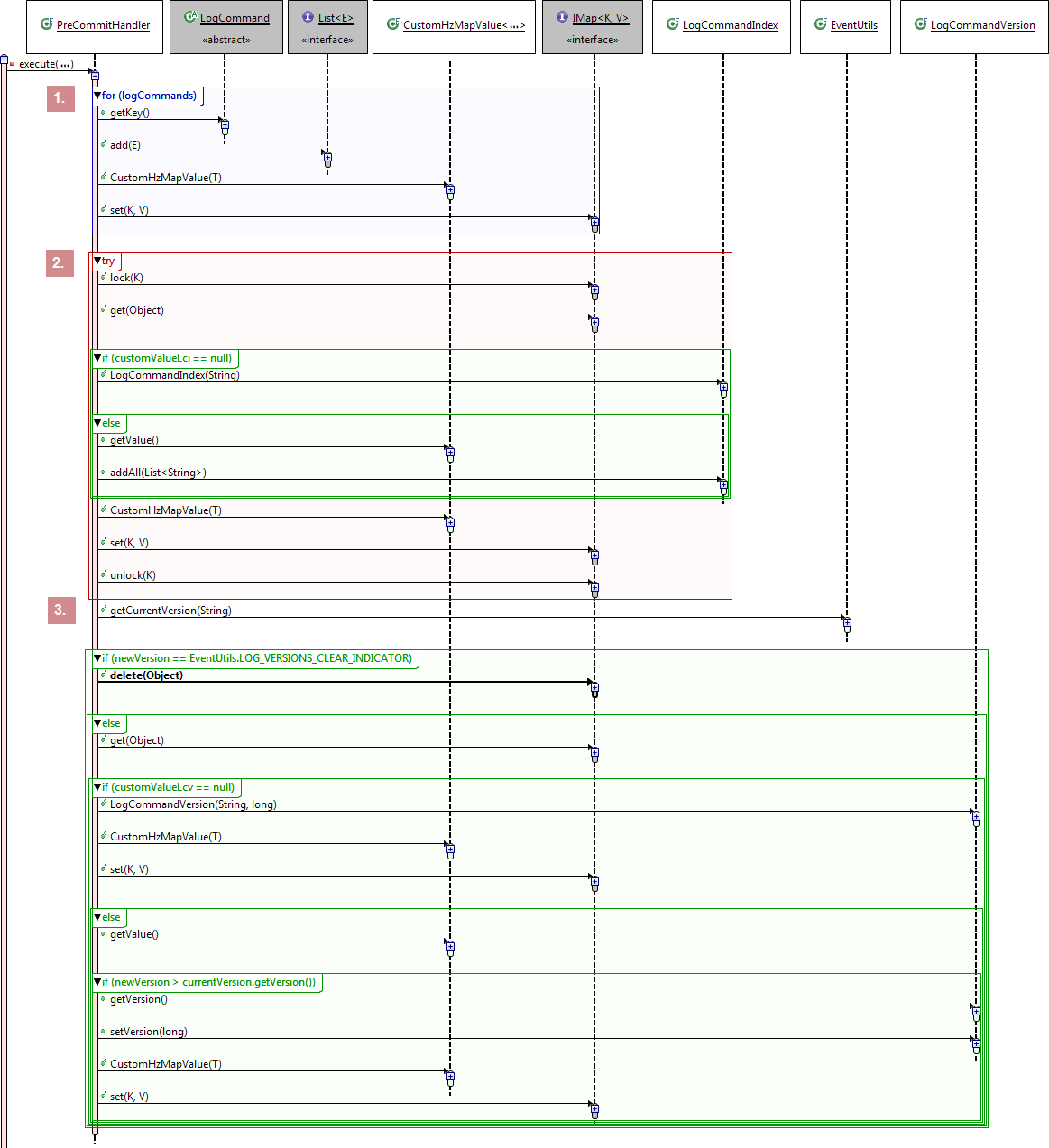
Figure 8: Collecting details: Sequence Diagram (simplified)
Sequence:
- Get all thread-local "logCommands". Add them to a local list. Store the "logCommand" to the "logCommands" map.
- Lock the "logCommandIndexes" map with the current process instance ID. Get the "logCommandIndexes" entry. Create a new one if it doesn't exist. Append the local list. Put the index back to the distributed map. Unlock.
- Get the current max version for this process instance from the distributed map. If no longer needed, delete it; otherwise, update and rewrite.
Storing
As described earlier, each node is responsible for storing a subset of process instances into the database. The key for distributing the instances is the Process Instance ID. Each node has one or more consumer threads which takes commands out of the queue and stores them into the database. To avoid conflicts between multiple local threads, a local locking mechanism is in place (a synchronized map).

Figure 9 : Storing details (simplified)
Sequence:
- Get the local set of process instances and loop through them.
- Lock the current process instance. If already locked, take the next free one.
- Get the "logCommandIndex" for this process instance.
- Loop through all "logCommands" and
- Save them to the database.
- After committing the batch, lock the "logCommandIndexes" map. Get the "logCommandIndex" for this process instance. Remove all previously processed entries.
- If there are entries left, write the new collection back to the "logCommandIndexes" map; otherwise, delete the entry.
- Unlock the current process instance.
Process Data Filter for Persistence
If configured, a process' data is persisted when completed ("processaudittrail.process.data.strategy") regardless of how the process completed (e.g., regular, canceled, deleted by an admin, etc.).
All data defined on the outermost process (also called "root process") qualifies for persistence. If you do not want to persist certain data, follow the filter options below. These filters also apply when you fetch data using the functions for displaying entries.
Variable Filter on Process
-
Example of Process Variables
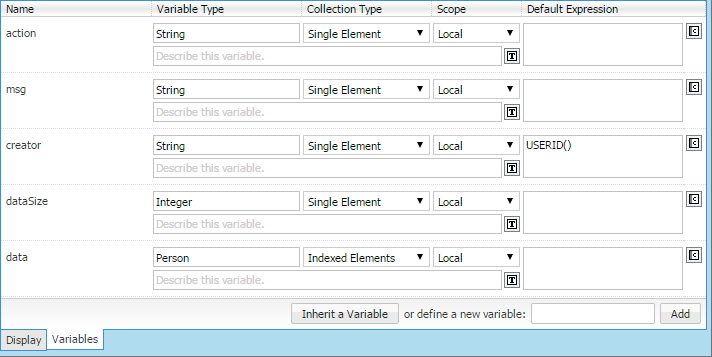
Figure 10 : Example variables
-
Filtering the variable value of "data" Open the Meta Data editor of the Process business object and add "ProcessAuditTrail-Exclude" as key and "data" as value.
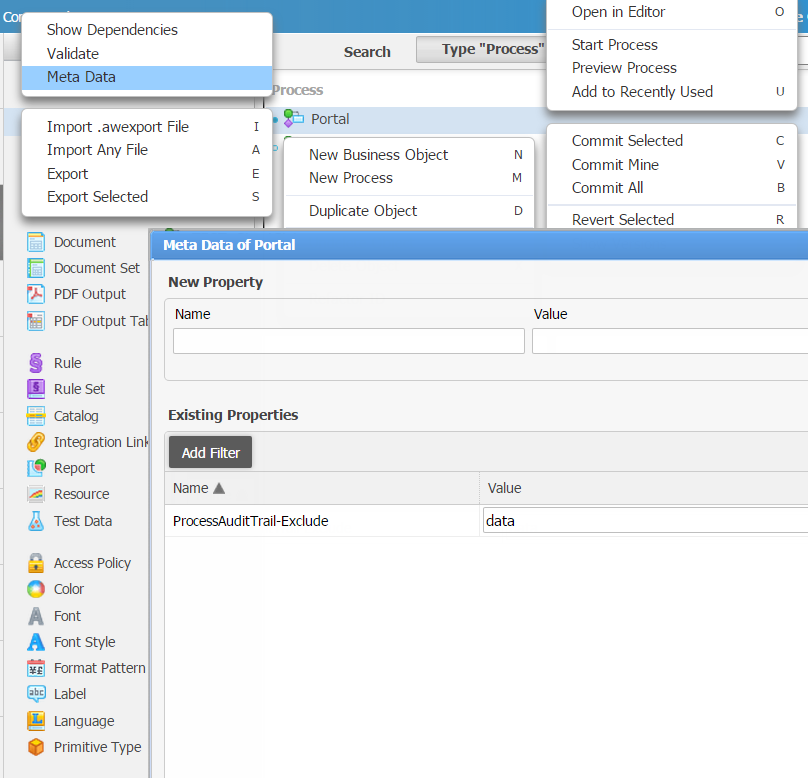
Figure 11: Variable Filter on Process
-
If you want to filter multiple variables, add a comma-separated list of variable names.
-
If you want to filter all variables, enter the wildcard character ("*").
Property Filter on Data Class
-
Example of Data Class definition
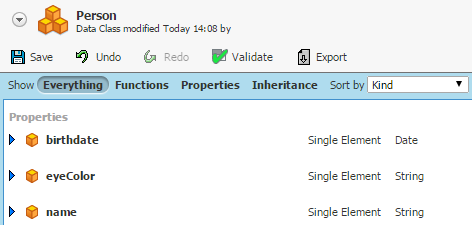
Figure 12: Example Data Class definition
-
Filter the property "eyeColor" Open the Meta Data editor of the Data Class business object and add "ProcessAuditTrail-Exclude" as key and "eyeColor" as value.
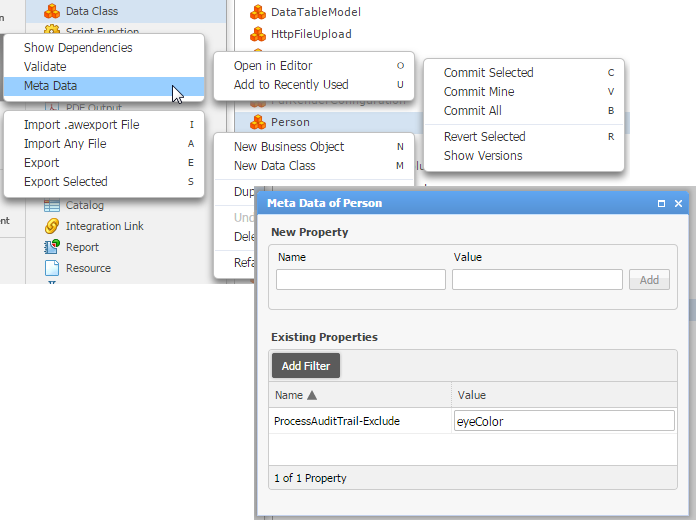
Figure 13: Property Filter on Data Class
-
If you want to filter multiple properties, add a comma-separated list of property names.
-
If you want to filter the whole Data Class, enter the wildcard character ("*").
Configuration and Setup
Configuring the Server
Appway needs an additional Hazelcast configuration. It changes the partitioning strategy in such a way that keys are scanned for an "@". Only the part after this character is used to evaluate the owning partition.
In your installation, go to the <data home>/conf directory. Add the following to the hazelcast.xml file:
<hazelcast …>
…
<properties>
…
<property name="hazelcast.partitioning.strategy.class">
com.hazelcast.partition.strategy.StringAndPartitionAwarePartitioningStrategy</property>
…
</properties>
…
</hazelcast>
Make sure you apply this configuration on all your nodes.
Configuring the Cluster Storage
Appway supports different kinds of storage mechanisms for its distributed maps. Apply one of the following configurations depending on the type of storage you have. This configuration, however, does not set the data storage for the log entries.
File System
No special configuration is needed.
Relational Database
To use this extension with the RelationalDbHazelcastStore extension, manually add the new database tables.
- Connect to your database. You must have rights to add tables and indexes.
- Follow the steps described in the System Installation article corresponding to your Platform version and adapt the SQL statements accordingly for the following table names:
- "logcommands"
- "logcommandindexes"
- "logcommandversions"
Cassandra
To use this extension with the CassandraDataStore extension, manually add the new database tables.
- Connect to your Cassandra installation. You must have rights to add tables.
- Follow the steps described in the System Installation article corresponding to your Platform version and adapt the SQL statements accordingly for the following table names:
- "logcommands"
- "logcommandindexes"
- "logcommandversions"
Configuring the Extension
There are two ways to configure the extension:
- Via the Appway Studio When all nodes are up and running, go to Extensions > Permanent Extensions > ProcessAuditTrail [right click] > Edit Configuration. The configuration becomes active after the next restart. To have the same configuration active on each node, restart the whole cluster, not just the single nodes.
- Via the "ProcessAuditTrail.jar.cfg" file Create or edit the configuration file "<data home>/extensions/ProcessAuditTrail.jar.cfg" manually. Ensure that the configuration is applied on each Appway cluster node.
Data Collection Properties
Properties define which and how each piece of data is collected. The amount of data generated depends on your solution. There is always a "strategy" and a "log" property:
- "strategy" defines if an entry should be stored in the database table. If historized, it keeps the complete history of a value; if not, only the latest value is kept.
- "log" defines if a human-readable log message should be generated and stored in the "audit_log" database table.
For more information on collected data stored in the database, see the chapter on Entity Relationship Diagram.
| Configuration Property | Description |
|---|---|
| processaudittrail.version.filter.strategyn(String) | Version Filter strategynHow to log changes if a process instance's version filter changesnAffected database table: version_filternValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault: KeepHistory |
| processaudittrail.version.filter.logn(Boolean) | Version Filter lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance's version filter changesnAffected database table: audit_lognValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.process.instance.status.strategyn(String) | Process Instance Status strategynHow to log changes if a process instance's status changesnAffected database table: process_instance_statusnValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault: Ignore |
| processaudittrail.process.instance.status.logn(Boolean) | Process Instance Status lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance's status changesnAffected database table: audit_lognValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.process.instance.attribute.strategyn(String) | Process Instance Attribute strategynHow to log changes if a process instance's attribute is added, modified or removed.nAffected database table: process_instance_attributenValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault: KeepLatest |
| processaudittrail.process.instance.attribute.logn(Boolean) | Process Instance Attribute lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance's attribute is added, modified or removednAffected database table: audit_lognValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.token.attribute.strategyn(String) | Token Attribute strategynHow to log changes if a process instance token's attribute is added, modified or removednAffected database table: token_attributenValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault: KeepLatest |
| processaudittrail.token.attribute.logn(Boolean) | Token Attribute lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance token's attribute is added, modified or removednValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.token.status.strategyn(String) | Token Status strategynHow to log changes if a process instance token's status changesnAffected database table: token_statusnValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault: Ignore |
| processaudittrail.token.status.logn(Boolean) | Token Status lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance token's status changesnAffected database table: audit_lognValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.token.user.strategyn(String) | Token User strategynHow to log changes if a process instance token's user assignment changesnAffected database table: token_usernValid values: Ignore, KeepLatest, KeepHistorynDefault value: KeepHistory |
| processaudittrail.token.user.logn(Boolean) | Token User lognWhether to log a human-readable log message if a process instance token's user assignment changesnAffected database table: audit_lognValid values: true, falsenDefault: true |
| processaudittrail.process.data.strategyn(String) | Process Data strategynHow to log a process instance's root process data on process completion, termination or cancellationnValid values: Dispose, StorenDefault: Dispose |
Other Properties
| Configuration Property | Description |
|---|---|
| processaudittrail.data.sourcen(String) |
The Appway Data Source to be used to store the process audit log entriesnNote: Ensure it is available on startup. Default: ProcessAuditTrail |
| processaudittrail.auto.migrate.databasen(Boolean) |
Whether to auto-migrate database changes or not "Database changes" refer to the initial table and index creation and potential future updates of database objects. Set to false if your database user does not have DDL change rights.nIf set to false and there are pending changes, the extension startup is prevented and a file with all the changes is written to a temporary location. The exact location is written to the log. Valid values: true, false Default: true |
| processaudittrail.listener.priorityn(Integer) |
The event listener's priority for receiving event notificationsnEnsure that other listeners that will modify data will be called after this listener. Check your system documentation about what such a listener does and its priority; otherwise, the audit messages could get messed up.nA listener implements the Java interface "com.nm.sdk.data.processes.listener.ProcessListener".nMeaning: The lower the priority, the later it will be called. Valid range :-2147483647 - 2147483647, intended 1-100 Default: 10 |
| processaudittrail.async.logger.countn(Integer) |
Number of asynchronous loggers (consumers /DB worker threads). nProvide enough DB connections (connection pool size) since each thread will keep one all the time. Valid values: 1 - 2147483647 Default: 5 |
| processaudittrail.async.logger.priority |
Asynchronous logger's Java thread prioritynThere are open issues with thread priorities in Java and Linux. At its current state, it only works under the following conditions:
Meaning: Threads with higher priority are executed before other threads with lower priority. Valid range: 1 - 10 Default: 7 |
| processaudittrail.sync.versions.on.startup (Boolean) |
Whether to synchronize the max version per process instance from the database on startup or not. This may be a very time-consuming task and delays the startup until all non-completed process instances versions are synchronized. This feature is disabled by default since all data is assumed to be in sync. To avoid corrupted log data, enable it when "processaudittrail.cluster.logCommandVersion.persistent" is set to false. Note: You need to run the extension with this feature enabled at least once in case of migrations from earlier versions. Valid values: true, false. Default value: false |
| processaudittrail.sync.versions.tables (String) |
Configure the tables you want to use as input for the database sync (on startup ("processaudittrail.sync.versions.on.startup" set to true) or via job (schedule set via "processaudittrail.sync.versions.job.schedule")). Cover the tables needed (depends on the data collection properties used). If enabled, the tables "process_instance" and "process_instance_status" are processed by default. Valid values: version_filter, process_instance_attribute, audit_log, token, token_attribute, token_status, token_user. Default: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.sync.versions.job.schedule (String) | Define an automated job to synchronize the max versions from the database. This job will be registered after a successful extension startup and, if clustered, will run only on one node. Note: While the job is running, all access to the "logcommandversionsmap" will start using distributed locks. This decreases the throughput to write data to the database. This job is not needed during regular operation. You should only enable it if Appway Support suggests you to do so. Valid values: Valid cron job pattern, e.g., daily at 2am: 0 0 2 * * ?. Default: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.cluster.logCommand.persistent |
Whether to enable persistence for the logCommands and logCommandIndexes map or not. If you have a file system storage (local or NFS) in use and have a high load or very high I/O, set this parameter to false. The drawback is that you lose persistence for log entries which, in worst case, leads Process Audit Trail data loss (i.e., those that have not yet been written to the database). Note: Changing this value only has an effect when restarting the whole cluster. Valid values: true, false. Default: true |
| processaudittrail.cluster.logCommandVersion.persistent (Boolean) |
If you are willing to accept longer startup times, disable the persistence of the "logCommandVersions" map (same reasons as those mentioned for "processaudittrail.cluster.logCommand.persistent"). If you disable it, you must enable the sync on startup option by setting "processaudittrail.sync.versions.on.startup = true". Valid values: true, false. Default: true |
| processaudittrail.database.connection.retry.count.on.startup (Integer) |
During startup, the number of times a database reconnect is tried before an exception is thrown. Note: There is a two-second pause between a failure and a retry. Therefore, a retry count of 4 means a possible wait time of up to 8 seconds before an exception is thrown. Meaning: -1 = endless, else retry count. Valid values: -1 - 2147483647 (-1 means endless). Default: 1 |
| processaudittrail.async.logger.reconnect.after (Integer) |
How many log commands shall be written by an asynchronous logger until the database connection is returned to the connection pool and a new one is requested. Meaning: 0 = never, else write count. Valid values: 0 - 2147483647. Default value: 0 |
| processaudittrail.async.logger.transaction.size (Integer) |
Sets the maximum size of a database transaction before a commit is issued. Use a low value if there are only a few commands per Process Instance left to process. The lower the number, the more updates and locks take place on the distributed map 'logCommandIndexes'. This can become expensive and end in bad throughput. As an option, you can increase the number of writer threads, but this does not reduce the load on the distributed map ('processaudittrail.async.logger.count'). Valid values: 1 - 2147483647. Default value: 30 |
| processaudittrail.getMaxVersions.parallel.degree.hint (String) |
When evaluating the maximum version used per Process Instance, you can provide a parallel degree hint for the query. This can be necessary if you have a huge amount of data to process and want to optimize performance. Ask your DBA for more details. Example value for Oracle: /*+ PARALLEL(12) */. Example value for MS SQL Server: OPTION (MAXDOP 12). Meaning: [empty] = database or table default, otherwise the hint you provide. Valid values: Database dependent hint. Currently available for Oracle and MS SQL Server. Default value: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.business.object.caches.invalidation.time (Integer) |
Business Object caches invalidation time. All Business Objects used by this extension are reloaded after this timeout [s]. Its values are cached. All Business Objects will be read using the LatestCommittedFilter, meaning it uses the latest committed version of a Business Object. All used Business Objects can be identified using the dependency view on the Appway Studio. Meaning: Seconds. Valid values: 1 - 2147483647. Default: 300 |
| processaudittrail.languages.full.locale (Boolean) |
Whether to log messages with full locale support or not. For example, if you installed Appway languages de, de_CH, en, en_US, en_CA and the configuration is set to "false", it will work only with de, en. If set to "true", it will work with all of them. Note: This setting has an effect on the number of columns used in the database tables and amount of data written. Valid values: true, false. Default: false |
| processaudittrail.skip.injected.processes (Boolean) |
Disable audit trail on injected processes (with or without Swimlanes). Valid values: true, false. Default value: true |
| processaudittrail.user.system (String) |
String to use as system user ID. Valid values: any string. Default: System |
| processaudittrail.user.id.preference (String) |
If your company's real user ID is not the same as Appway's, provide an Appway user preference name which contains the real user ID. That ID is used in log entries instead of Appway's user ID. Valid values: An existing user preference name. Default: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.group.display.text.function processaudittrail.role.display.text.function (String) |
If your role/groups use artificial names, provide script function names which can resolve a role/group ID into a preferred display text. This text is used in log entries instead of Appway's group/role names. It will always use the latest committed version of those script functions. Valid value: A name of a script function taking the role/group ID as parameter and returns a display text string. Default: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.element.name.prepend.pattern |
Provide a regular expression pattern which will be applied to an element's Name field (set via the Process Editor). The regular expression's first found result is prepended to the element's Task List Name and is saved as the element's name in the database. If prepended, there will be a separator: ' - '. Valid value: A regular expression following the rules of the Java class Pattern. Default: [empty] |
| processaudittrail.shutdown.behavior (String) |
Define what should happen on an extension shutdown
Note: In cluster mode, other nodes can still produce entries which will be processed on this node. This blocks a shutdown on this node until the others go down, too. |
| processaudittrail.shutdown.behavior.delay (Integer) |
If "processaudittrail.shutdown.behavior = delayedDatabase", define a delay [ms]. After that time, storage is suspended and the remaining entries are stored and processed on the next startup (if persistence is enabled). Meaning: Milliseconds Valid values: 0 - 2147483647 Default: 120000 |
Configuring Content
Labels
This extension uses the following Labels to log events. By default, they're installed in English ("en") and German ("de"). If you need more translations or if you want to change the existing message, simply add the new content the same way you would for any other Label business object. Some Labels use placeholders such as "$1" or "$2". The descriptions below are also found in Appway Studio on the Label's property tab ("Description").
- ProcessAuditTrail_AdminPrefix
- ProcessAuditTrail_AttachedCancelIntermediateEventTriggered
- $1: Type
- ProcessAuditTrail_AttachedErrorIntermediateEventTriggered
- $1: Type
- ProcessAuditTrail_AttachedMessageReceiveIntermediateEventTriggered
- $1: Type
- ProcessAuditTrail_AttachedSignalReceiveIntermediateEventTriggered
- $1: Type
- ProcessAuditTrail_AttachedTimerIntermediateEventTriggered
- $1: Type
- ProcessAuditTrail_DueDateExpired
- ProcessAuditTrail_DynamicElementId
- ProcessAuditTrail_PreviousTokenAttributesCopied
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessCompleted
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessDeleted
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInjected
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributeAdded
- $1: Attribute name
- $2: Value
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributeModified
- $1: Attribute name
- $2: Old value
- $3: New value
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributeRemoved
- $1: Attribute name
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceRestored
- $1: Original last modification date
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceStatusChanged
- $1: Old state
- $2: New state
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkSourceIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkSourceIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkSourceIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkTargetIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkTargetIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessLinkTargetIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageReceiveIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageReceiveIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageReceiveIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageSendIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageSendIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessMessageSendIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessNoneIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessNoneIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessNoneIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessReactivated
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalReceiveIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalReceiveIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalReceiveIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalSendIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalSendIntermediateEventRegistered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessSignalSendIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessStarted
- $1: Starter's user ID
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTimerIntermediateEventCancelled
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTimerIntermediateEventRegistered
- $1: Date
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTimerIntermediateEventTriggered
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenAdded
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenAssigned
- $1: Previous user ID
- $2: New user ID
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenAttributeAdded
- $1: Attribute name
- $2: Value
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenAttributeModified
- $1: Attribute name
- $2: Old Value
- $3: New value
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenAttributeRemoved
- $1: Attribute name
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenRemoved
- ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessTokenStatusChanged
- $1: Old state
- $2: New state
- ProcessAuditTrail_TakeOwnershipFromGroup
- $1: From group
- ProcessAuditTrail_TakeOwnershipFromRole
- $1: From role
- ProcessAuditTrail_VersionFilterChanged
- $1: Old version filter
- $2: New version filter
Process Filter
By default, the extension will record events for all persistent Appway processes, i.e., all root processes with Swimlanes. During the very first startup, the extension installs a "ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessFilter" catalog where you can define the process ID filter rules for your solution.
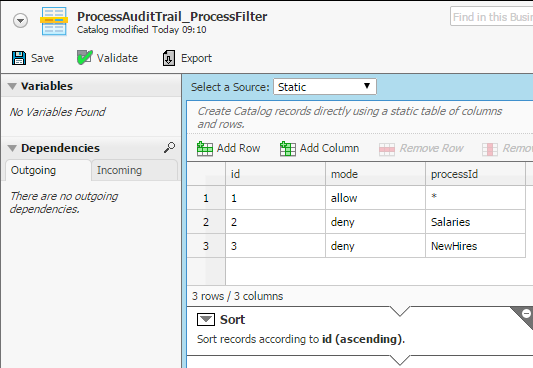
Figure 14: Process Filter example
Filter processing rules:
- The records are processed in the order received.
- To explicitly add a process ID, use the keyword "allow".
- To explicitly skip a process ID, use the keyword "deny".
- The wildcard character ("*") adds or skips all currently existing processes.
- The filter rules are processed and cached. The cache is cleared frequently and the rules will be re-evaluated (see configuration property "processaudittrail.business.object.caches.invalidation.time").
- The latest committed version of this catalog is always used.
- You can change the definition of the catalog but it must at least contain the columns "mode" and "processId".
Database
A database stores the log entries.
Supported Databases
For a list of supported databases for your Appway version, see the Technical Requirements article.
Database Configurations
Certain databases need a special configuration to make the extension work as expected.
MS SQL Server
Connect as a DBA and issue the following commands:
- ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET READ_COMMITTED_SNAPSHOT ON
- ALTER DATABASE <database name> SET ALLOW_SNAPSHOT_ISOLATION ON
DDLs and DMLs
All DDLs and DMLs used inside the extension are contained in a text and XML file. If you extract the extension's JAR file, go to:
- DDL: "db/ddl/<version>/<database vendor>.sql" It is possible to have multiple versions to support an automated upgrade process. Version 1 is the initial version; all others are subsequent ones. To check the currently installed version, query the "db_info" table.
- DML: "db/sql/<database vendor>.xml"
Auto-Migration
By default, all database objects used by this extension are installed automatically. Future database changes can be automated as well. See the section on configuring the "processaudittrail.auto.migrate.database" property.
If auto-migration is enabled but the database user does not have the right to execute DDLs, the extension startup will fail. In Appway's log files, find a file system path to a temporary file containing the needed DDL statements, which you can then execute manually.
Languages
Appway supports multiple languages for solutions and the same is true for logged messages and events. The Labels used can change over time, but log messages always log using the Labels valid at the time of the event. Therefore, the Labels are translated and stored in multilingual versions in the database.
At first startup, the extension installs all database tables needed. Some tables contain columns which store data in multiple languages. In the Entity Relationship Diagram, there are table columns with the postfix placeholder "_". This placeholder is replaced by the concrete languages used in your solution (one column per language). If you add a new language to your solution, the extension tries to create additional database table columns. If auto-migration is disabled, it creates a temporary file which you can execute manually.
Entity Relationship Diagram
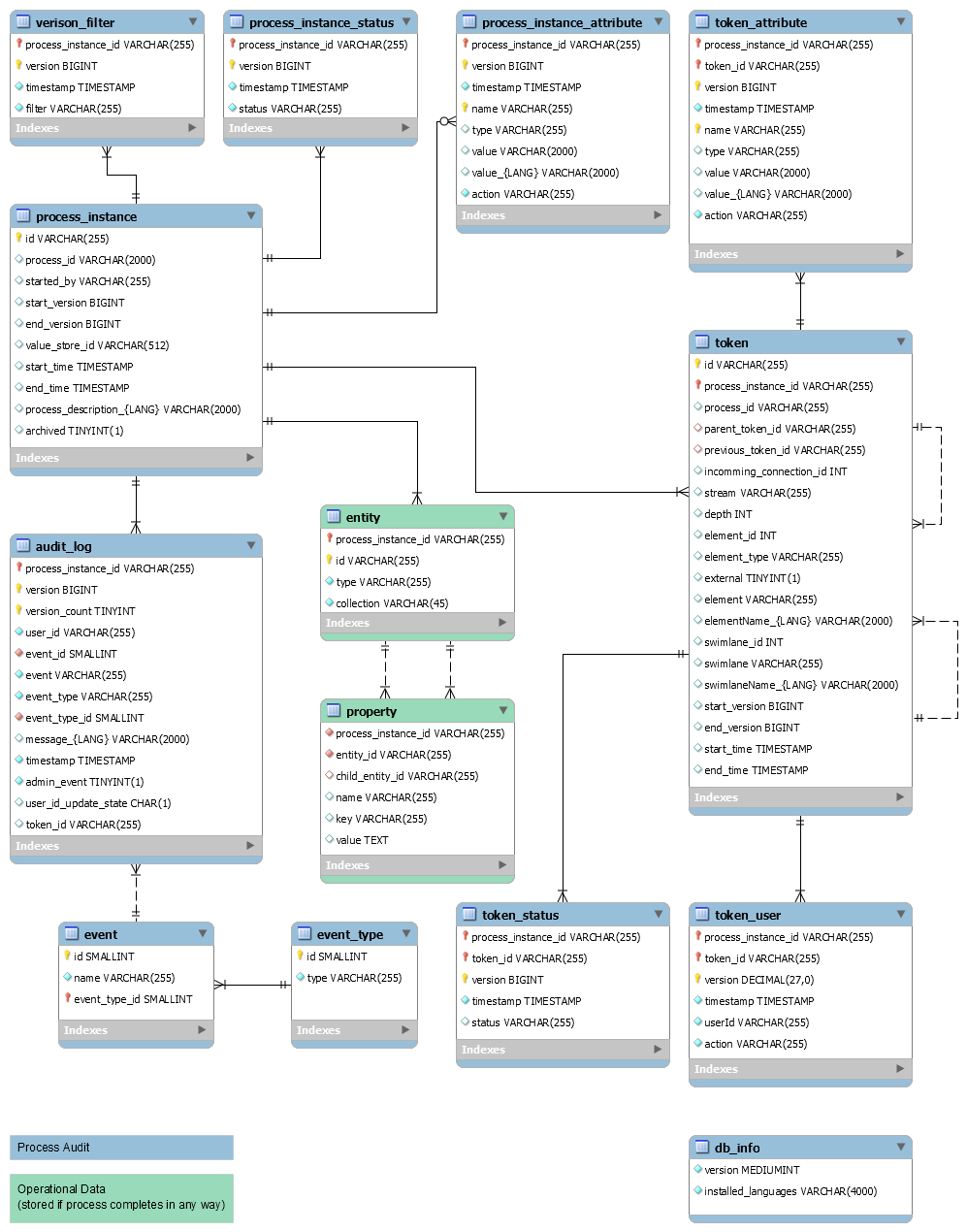
Figure 15: Entity relationship diagram
Database Tables in Detail
The "version" column name represents a simple sequence for each process instance and it starts at 1. This is necessary because timestamps do not provide enough resolution to generate unique entries. In Appway, the versions are cluster-wide and are maintained outside of the database via the distributed map "logCommandVersions".
"process_instance"
Contains basic data about the running process instance. Other tables directly or indirectly relate to this table via the process instance ID.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| process_id | The process' ID |
| started_by | The user ID of the user that started the process |
| start_version | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| start_time | Timestamp when the process was started |
| end_version | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| end_time | Timestamp when the process was completed |
| value_store_id | ID of the Value Store used by the process |
| process_description_ | The process' description (multilingual) |
| archived | The ProcessAuditTrail extension just collects data but never deletes. Use this flag when archiving or deleting collected data. |
"audit_log"
Contains all generated event log messages in multiple languages.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| version_countn(PK) | There are some events which produce more than one log entry. To be able to insert unique messages, a second sequence is needed. |
| user_id | The user ID this log message belongs to |
| event_id | The ID of the event |
| event | Description of the event |
| event_type_id | The ID of the event category |
| event_type | Description of the event category |
| message_ | The log message. There is one column for each installed language. |
| timestamp | Timestamp when the log message was created inside Appway |
| admin_event | Indicator if this log message is based on an administration action or not |
| user_id_update_state | Reserved for future use |
| token_id | If this log message is somehow related to a token, the token ID will be stored. |
"version_filter"
Contains all version filters with which a process instance was running.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| version | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this version filter was set |
| filter | A string representation of the version filter used |
"process_instance_status"
Contains the process instance's status.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this process instance status was set |
| status | The process instance status |
"process_instance_attribute"
Contains the process instance's attributes and its values. The values are converted into a string representation before storing them into the database.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this process instance attribute was modified |
| namen(PK) | Timestamp when this process instance status was set |
| type | Java type of the value, e.g., when the value is a string, the type would be "java.lang.String". |
| value | The plain, untranslated value. |
| value_ | The value translated into different languages |
| action | Modification action. This is relevant if data is stored historized. If so, it will contain entries like "added", "updated", "deleted", etc. |
"token"
Contains all information about a token.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| idn(PK) | The token ID |
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| process_id | The process' ID. In this case, it will be a Sub-Process ID. |
| parent_token_id | The parent token ID |
| previous_token_id | The previous token ID |
| incomming_connection_id | The ID of the connection this task was reached |
| stream | An artificial number identifying parallel streams, e.g., after an AND gateway. If there's no parallel stream, this column is null. |
| depth | If on the level of the root process "1"; otherwise, the nested depth of this token. |
| element_id | The ID of the element in the Process this token was created for |
| element_type | The type of the element in the Process this token was created for |
| external | Indicator if the element in the Process this token was created for is completed by an external system. "external" means outside of Appway and is usually a human task (e.g., a Screen or Placeholder task). |
| element | The element's name (defined via Process editor) |
| element_name_ | A description of the element by using its Task List Name, Description and Name |
| swimlane_id | The ID of the Swimlane in the Process this token was created for |
| swimlane | The Swimlane's name (defined via Process editor) |
| swimlane_name_ | A description of the Swimlane using its Task List Name, Description and Name |
| start_version | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| start_time | Timestamp when the process was started |
| end_version | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| end_time | Timestamp when the process was completed |
"token_status"
Contains the token's status.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| token_idn(PK) | The token ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this token status was set |
| status | The token status |
"token_attribute"
Contains the token's attributes and its values. The values are converted into a string representation before storing them into the database.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| token_idn(PK) | The token ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this token attribute was modified |
| namen(PK) | Timestamp when this token status was set |
| type | Java type of the value, e.g., when the value is a string the type would be "java.lang.String". |
| value | The plain, untranslated value |
| value_ | The value translated into different languages |
| action | Modification action. This is relevant if data is stored historized. If so, it will contain entries like "added", "updated", "deleted", etc. |
"token_user"
Contains the token's user assignment.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| token_idn(PK) | The token ID |
| versionn(PK) | Per process instance unique sequence value |
| timestamp | Timestamp when this token status was set |
| user_id | The user assigned to the token |
| action | Modification action. This is relevant if data is stored historized. If so, it will contain entries like "added", "updated", "deleted", etc. |
"entity"
Contains the root process' data which is available after reaching its end. It describes the data and collection type.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_idn(PK) | The process instance ID |
| idn(PK) | An artificial ID identifying this entity |
| type | Appway data type. The root entry has the value "ProcessAuditTrail_Root". |
| collection | The collection type: "none", "indexed" or "mapped" |
"property"
Contains the root process' data which is available after reaching its end.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| process_instance_id | The process instance ID |
| entity_id | Reference to the entity this property belongs to |
| child_entity_id | If this property has a child or not. A property value is a child. |
| name | The property's name |
| key | If "mapped", the key; if "indexed", the index; Otherwise, Null . |
| value | The property's value |
"event_type"
Reference data table which defines event categories.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| idn(PK) | Ascending ID of an event type |
| type | The event's type |
"event"
Reference data table which defines event categories.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| idn(PK) | Ascending ID of an event type |
| name | The event's name |
| event_type_idn(PK) | The event's type ID |
"db_info"
Contains information about the currently installed version. It is used for automatic migrations and multiple language support. Do not change the content of this table.
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| version | The installed version of the extension's database model |
| installed_languages | The languages currently installed in the database. If new languages will be added to Appway, those have to be installed into the database as well. |
Functions
Storing Data
ProcessAuditTrail_LogCustomEvent
This function allows you to add any custom log entry to the audit database. You can use it from anywhere you like and log any message you like.
As an alternative, you can use the ProcessAuditTrail_LogCustomEvent Trackpoint.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| MessagesnNamed String | Named collection of message texts for the corresponding languages. Use "$1" as placeholder for the user ID in the message.nExample: "{'en'='English text', 'de'='Deutscher Text', 'fr'='Texte français', 'it'='Testo italiano'}:String" |
| processInstanceIdnString, optional | An optional process instance ID for this log entrynBy default, the current process Instance ID will be used. If you call this function from outside a process instance and do not provide a process instance ID, it will raise an exception.nExample: "123456789012" |
| userIdnString, optional | An optional user ID for the log entrynBy default, the current user ID will be used. nExample: "superUser" |
| eventTypeIdnInteger, optional | An optional event type ID for the log entry. By default, value 6 (“Custom”) is used. The corresponding event type entry must be present in the event_type table. |
| eventIdnInteger, optional | An optional event ID for the log entry. By default, value 13 (“Custom event”) is used. The corresponding event entry must be present in the event table. |
| tokenIdnInteger, optional | An optional token ID for the log entry. By default, the token ID of the current context is used (if available). Otherwise, null is used. |
Reading Data
No generic viewer is available because each customer has different needs. However, some helper functions are provided to read and display data. Data is loaded from either live process instances or from the database (completed process instances). The functions return the same data structures so you only have to build a viewer once. The following are examples for loading and displaying data.
-
Load data
Copy//load log data
Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log $auditLog;
$auditLog := ProcessAuditTrail_LoadAuditLog($processInstanceId, false);
//load process instance attribute data
ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $piAttrs;
If $live Then
$piAttrs := ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLiveProcessAttributes($processInstanceId);
Else
$piAttrs := ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLoggedProcessAttributes($processInstanceId);
End
//load process data
ProcessAuditTrail_Scope $scope;
If $live Then
$scope := ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLiveProcessData($processInstanceId);
Else
$scope := ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLoggedProcessData($processInstanceId);
End -
Prepare for log message view
Copy//initialize log items
Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log $logItems := ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAuditLogToList($auditLog);
//sort items
ProcessAuditTrail_Log $i1;
ProcessAuditTrail_Log $i2;
SORT($logItems, $i1.version.compareTo($i2.version), $i1, $i2, true); -
Prepare for process instance attribute view
Copy//initialize attribute items
Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $attributeItems := ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAttributesToList($wfAttributes); -
Prepare for process data view
Copy//initialize data items
Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem $dataItems := new Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem;
ProcessAuditTrail_Scope $s;
If $scope.name == 'Root' Then
ForEach $s In $scope.subScopes Do
$dataItems.addAll(COMMON_AUDIT_NestedScopesToList($s));
End
Else
$dataItems.addAll(COMMON_AUDIT_NestedScopesToList($scope));
End -
Helper Script Functions
Copy
Function ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAuditLogToList(Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log $nested, Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log $list := null, Integer $indentLevel := 0, String $pathPrefix := null) : Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log Begin
If $nested == null Then
Return $list;
End
//
If $list == null Then
$list := NewIndexed(ProcessAuditTrail_Log);
End
//
ProcessAuditTrail_Log $logItem;
String $itemPath;
Integer $i;
//
For $i := 1 Condition $i <= $nested.size() Step $i := $i + 1 Do
$logItem := $nested[$i];
$itemPath := CONCAT($pathPrefix, '/', TOSTRING($i));
$logItem.indentLevel := $indentLevel;
$logItem.itemPath := $itemPath;
$list.addElement($logItem);
ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAuditLogToList($logItem.children, $list, $indentLevel + 1, $itemPath);
End
//
Return $list;
EndCopy
Function ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAttributesToList(Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $nested, Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $list := null, Integer $indentLevel := 0, String $pathPrefix := null) : Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes Begin
If $nested == null || $nested.size() == 0 Then
Return $list;
End
If $list == null Then
$list := NewIndexed(ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes);
End
ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $attributes;
ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes $clonedItem;
String $itemPath;
ForEach $attributes In $nested Do
$itemPath := CONCAT($pathPrefix, '/', $attributes.name);
$clonedItem := CLONE($attributes, false, false);
$clonedItem.indentLevel := $indentLevel;
$clonedItem.itemPath := $itemPath;
$list.addElement($clonedItem);
ProcessAuditTrail_NestedAttributesToList($attributes.children, $list, $indentLevel + 1, $itemPath);
End
Return $list;
EndCopy
Function ProcessAuditTrail_NestedScopesToList(ProcessAuditTrail_Scope $scope, Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem $list := null, Integer $indentLevel := 0, String $pathPrefix := null) : Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem Begin
If $scope == null Then
Return $list;
End
If $list == null Then
$list := NewIndexed(ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem);
End
String $scopePath := CONCAT($pathPrefix, '/', $scope.name);
//
ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem $scopeItem := new ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem;
$scopeItem.name := $scope.name;
$scopeItem.indentLevel := $indentLevel;
$scopeItem.children := CLONE($scope.variables, false, false);
$scopeItem.type := '%SCOPE%';
$scopeItem.itemPath := $scopePath;
$list.addElement($scopeItem);
//
If $scope.subScopes != null && $scope.subScopes.size() > 0 Then
If $scopeItem.children == null Then
$scopeItem.children := new Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem;
End
$scopeItem.children.addElement(new ProcessAuditTrail_DataItem);
End
//
ProcessAuditTrail_NestedDataitemsToList($scope.variables, $list, $indentLevel + 1, $scopePath);
ProcessAuditTrail_Scope $subScope;
ForEach $subScope In $scope.subScopes Do
ProcessAuditTrail_NestedScopesToList($subScope, $list, $indentLevel + IF($scope.variables != null && $scope.variables.size() > 0, 1, 1), $scopePath);
End
Return $list;
End
ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLiveProcessData
This function returns data from a live process. The data is collected from the in-memory instance, not read from the database.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| processInstanceIdnString | The process instance ID to load the live data from Example: "123456789012" |
| Return value | Description |
|---|---|
| ProcessAuditTrail_Scope | A data structure containing all of the process' live data |
ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLoggedProcessData
This function returns data from a completed process. This data is read from the database. The data can only be returned if the "processaudittrail.process.data.strategy" configuration is set to "store". If not, no data will be saved upon process completion.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| processInstanceIdnString | The process instance ID to load the live data from Example: "123456789012" |
| Return value | Description |
|---|---|
| ProcessAuditTrail_Scope | A data structure containing all of the process' live data |
ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLiveProcessInstanceAttributes
This function returns process instance attributes from a live process. The data is collected from the in-memory instance, not read from the database.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| processInstanceIdnString | The process instance ID to load the live data from Example: "123456789012" |
| Return value | Description |
|---|---|
| ProcessAuditTrail_ProcessInstanceAttributes | A data structure containing all of the process' live instance attributes |
ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLoggedProcessInstanceAttributes
This function returns process instance attributes from a completed process. The data is read from the database. The data can only be returned if the configuration "processaudittrail.process.instance.attribute.strategy" is set to "KeepLatest" or "KeepHistory". If not, no data will be saved.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| processInstanceIdnString | The process instance ID to load the live data from Example: "123456789012" |
| Return value | Description |
|---|---|
| ProcessAuditTrail_Scope | A data structure containing all of the process' live data |
ProcessAuditTrail_LoadLog
This function returns all log messages for a given process instance ID. The data is always read from the database.
The log detail level is defined via various configurations. See Data Collection Properties for more information. Entries may offer too much detail for a quick view so this function applies a static, predefined filter which contains:
-
Version filter changed
-
Process Instance status changed
-
(Sub-)Process Token status changed
-
Previous Process Token copied
-
Automatic Take Ownership from role/group
-
Process Instance Attribute added/modified/removed
-
(Sub-)Process Token Attribute added/modified/removed
-
Task opened/retained/taken over by user
-
Link Source/Target
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| processInstanceIdnString | The process instance ID to load the live data from Example: "123456789012" |
| unfilterednBoolean, optional | Whether to load the log messages and apply a static, predefined filter or notnDefault: falsenExample: "123456789012" |
| Return value | Description |
|---|---|
| Indexed ProcessAuditTrail_Log | A data structure containing all of the process' log messages |
Trackpoint
ProcessAuditTrail_LogCustomEvent
To avoid using explicit Script tasks or hard-to-find function calls inside other scripts or Screens, use the "ProcessAuditTrail_LogCustomEvent" trackpoint to add custom log entries instead of the function.
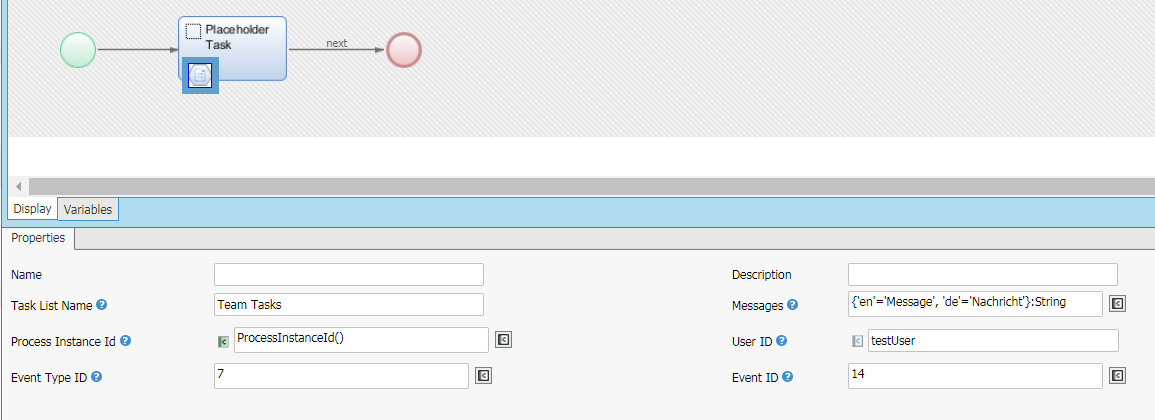
Figure 16: Custom Event Trackpoint
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| NamenString, optional | Standard component name property |
| DescriptionnString, optional | Standard component description property |
| Task List NamenString, optional | Name of this element if it appears in a Task List or elsewhere in the Workspace (may contain Language Labels) |
| MessagesnNamed String | Named collection of message texts for the corresponding languages. Use "$1" as placeholder for the user id in the message.nExample: ['en'='Now', 'de'='Jetzt']:String |
| Process Instance IdnString, optional | An optional Process Instance ID for the log entry. By default, the current Process Instance ID will be used.nExample: '123456789012' |
| User IDnString, optional | An optional user ID for the log entry. By default, the current user will be used.nExample: 'superuser' |
| Event Type IDnInteger, optional | An optional event type ID for the log entry. By default, value 6 (“Custom”) is used. The corresponding event type entry must be present in the event_type table. |
| Event IDnInteger, optional | An optional event ID for the log entry. By default, value 13 (“Custom event”) is used. The corresponding event entry must be present in the event table. |
GDPR Compliance
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is an EU regulation aimed at protecting the privacy of natural persons regarding the processing of personal data and the free movement of such data. The purpose of GDPR, among others, is to strengthen and to unify data protection laws within the EU for individuals, ensuring individuals have control of their personal data.
Important! The ProcessAuditTrail extension stores data and as such it can be used to persist information on data subjects (natural persons). Implementing a data persistence strategy that is compliant with the regulations stipulated by GDPR must be guaranteed by the implementation of the Solution by the customer or entity using this product. Compliance is not inherent in any way to the product itself.
This document and the content thereof and any information derived from it is not to be construed as legal, regulatory and/or tax advice. Appway is not permitted to and will not provide any legal, regulatory and/or tax advice. Appway is also not providing an interpretation of any laws or regulations that may be applicable to any customer, prospect, or anyone, and they shall be responsible for clarifying and stipulating the legal and regulatory requirements applicable to its business. While Appway personnel providing the services may, through experience or specialized training or both, be familiar with the general regulatory environment in their capacity as information-technology and management-consulting professionals, they will work under the direction of the customer and its legal counsels regarding the specific legal and regulatory requirements under which the customer operates. The compliance of the services and work results with the applicable laws and requirements remains the sole responsibility of customer and their legal, regulatory and/or tax advisors.