Managing Extensions
Introduction
Platform extensions are characterized by the .jar file extension, and are divided into:
- Restartable Extensions - They can be stopped and started while the Platform is running and they change the Platform behavior dynamically. Examples are: Functions, StatisticsCollector, and so on.
- Permanent Extensions - They cannot be stopped or started while the Platform is running, bu only when it is started or shut down. Examples are: WorkitemFinder, DataHistory, and so on.
- Secrets Manager Extensions - These extensions are used to provide integrations with external secrets managers. They are started before permanent extensions, and can be started or stopped at runtime. Examples are: AWSSecretsManage. See Secrets Management Framework documentation for more details.
Moreover, some extensions are mandatory for Platform installations. You can see the list of mandatory extensions in the System Installation guide or Product card corresponding to your Platform version.
Finally, consider that in FNZ Studio Composition, some modules or options are only visible if the corresponding extensions are installed, e.g., Data&Integration> Business Data Storage or Solution Maintenance > BAM. Moreover, some options in these modules may depend on:
- A specific Permission (e.g., the Business Activity Monitoring Permission to configure the BAM database). See details in the Advanced Permission document.
- A specific License (e.g., the Enterprise Development and Operations enabled by the BusinessObjectPatching extension and ProcessMigration extension).
Managing and Uploading Extensions from FNZ Studio Composition
The System Configuration > Extensions module in FNZ Studio Composition displays a list of all the restartable and permanent extensions currently available on your Platform.
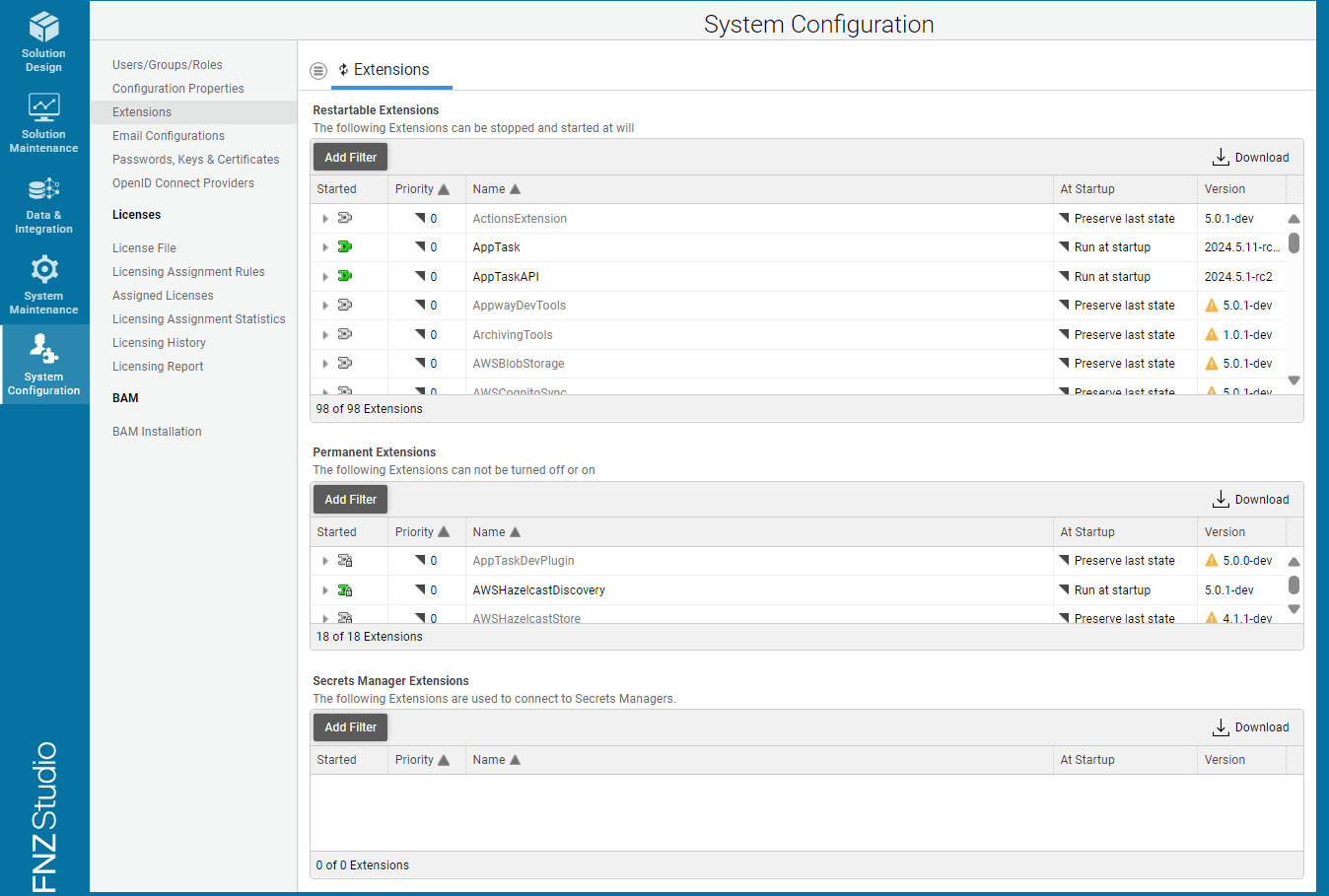
This modules is mainly used to:
- Edit an extension configuration - Right-click on the extension and select Edit Configuration. See each individual extension documents for details. Flawed extension configurations may generate validation messages (see below).
- Start or stop an extension - Right-click on the extension and select Start Extension/Stop Extension. The Started column provides information on whether the extension is started (green icon) or not started (gray icon).
- Upload or update an individual extension - Select Upload Extension from the menu icon in the top-left corner. See the Uploading Extensions section below for details.
- Check an extension version - The Version column provides version information.
- Check further extension information or validation messages - Click on the triangle icon to open the interline, which provides:
- The extension description
- The extension build date
- Deprecation messages (if any) - States if/when the extension was deprecated
- Validation messages (if any) - Shows:
- Warning/error messages in case of flawed extension configurations. Such validation also triggers an Extension Configuration Health Sensor (System Configuration > Health).
- Error messages in case of extensions with invalid file names (this applies both when uploading extensions from the Extensions module or from the Data Home).
Uploading Extensions
-
To upload an extension to the Platform, click on the the menu icon in the top-left corner, and select the Upload Extension option.
-
Make sure the extension has the proper name and is unique: one JAR file per extension, with the proper file name of the type OfficialExtensionName.jar (e.g.,
StatisticsCollector.jar) must be present. Any other redundant JAR files with custom characters or digits are not accepted and must be removed (e.g.,StatisticsCollector-1.2.3-2023.1.jar;StatsCollector.jar;Statistics-Collector.jar;StatisticsCollector-dev.jar).Note that, starting from FNZ Studio 2023.1, a validation mechanism is in place to prevent wrong or duplicated extension filenames. Invalid extension filenames trigger an Uploaded Failed error, and a message and a red icon are shown in the Extension interline (invalid extensions are shown first on the Extensions table): at this point, you can only delete or download such extension by clicking on the context menu.
-
To start the extension, right-click on it and select the Start Extension option from the context menu.
-
To specify the extension's behavior when the Platform is started, right-click on the extension and select the desired context menu item (the setting for each extension is displayed in the At Startup column of the list of extensions):
- Run At Startup - The extension is started when the Platform starts, regardless of if the extension was stopped or started when the Platform shut down.
- Do Not Run At Startup - The extension is NOT started when the Platform starts, regardless of if the extension was stopped or started when the Platform shut down.
- Preserve Current State (default) - If the extension was running before the Platform was shut down, it is started when the Platform starts, otherwise it is not started.
-
You can stop, download, or delete an extension by right-clicking on it and selecting the relevant option.
Deploying Extensions from Data Home
When installing or upgrading to a new Platform version, you can install or update all the necessary extensions from the <Local file system>/data-home/extensions directory.
While the deployment of Business Objects is a well-controlled process, because our Platform provides a versioning framework for Business Objects, which protects the running instances from newly deployed artifacts; on the contrary, the deployment of extensions requires more attention. Simply uploading an extension and restarting it can have unexpected results.
Any user interacting with the system and running operations which depend on an extension can experience failures while the extension is being restarted. However, just ensuring there is no user on the system while the extension is restarted is not sufficient.
There are various operations behind the scenes that are not transparent to the user. These are:
- Background jobs
- Process Engine threads
- Integration Links (file scanner, etc.)
If one of these operations depends on the extension that was stopped, the Process Instance can be suspended or other unexpected errors can occur. The purpose of this section is to describe two safe methods of deploying extensions.
Method 1: Shutdown and Restart
This is the preferred approach in deploying extensions. Follow these steps:
-
Shutdown all Platform nodes.
-
Replace the extension on all nodes by adding them to the
<Local file system>/data-home/extensionsdirectory. When updating extensions, make sure you update only the JAR files; any CFG files should remain the same as on system, in case you made any custom configurations. -
Make sure the extension has the proper name and is unique: one JAR file per extension, with the proper file name of the type OfficialExtensionName.jar (e.g.,
StatisticsCollector.jar) must be present. Any other redundant JAR files with custom characters or digits are not accepted and must be removed (e.g.,StatisticsCollector-1.2.3-2023.1.jar;StatsCollector.jar;Statistics-Collector.jar;StatisticsCollector-dev.jar). -
Start all Platform nodes. Note that an invalid extension filename triggers an error at startup and extension is not started.
-
Ensure the extensions are started in the Extensions module (invalid extension are shown first on the Extension table).
Note: Optionally, the extension can be uploaded at runtime, after which a server restart is required.
Method 2: Pause the Platform
This method implies pausing the serving of clients (instances remain up and running).
This is the approach to take when a server restart is not an option, for example when a Platform administrator has no permissions to restart the application server. This approach makes it possible to deploy an extension without a Platform restart, but at the cost of additional complexity. Follow these steps:
- Lock the application:
- Go to System Maintenance > System Overview > System Locking, and then click on the Lock Application button. This step prevents users from accessing the Workspace/ Studio Runtime. Note that while users cannot access the system, background jobs continue to run.
- Pause the schedulers on all nodes:
- Go to System Maintenance > System Overview > Job Scheduling, click on the menu icon on the top left, and select the Pause Schedulers on All Nodes option. This pauses background jobs and prevents new or upcoming jobs from being triggered.
- Stop all Process Engine threads:
- Go to Solution Maintenance > Processes > Process Engine > Process Threads, click on the menu icon on the top left, and select the Stop All Threads option. This stops all background actions on in-flight Process Instances.
- Stop Integration Links:
- Go to Data & Integration > Integration Link Management.
- Make a note of all running Integration Links.
- Stop all running Integration Links.
- Replace the extension to be deployed and restart it. To do so, follow these steps:
- In System Configuration >Extensions, click on the menu icon on the top left, and click on the Upload Extension button.
- Search for the extension .jar file and upload it.
- Right-click on the extension and click on the Start Extension button.
- Restart Integration Links:
- Go to Data & Integration > Integration Link Management.
- Start all the Integration Links you have previously stopped.
- Start all Process Engine threads:
-
Go to Solution Maintenance > Processes > Process Engine > Process Threads, click on the menu icon on the top left, and select the Start All Threads option.
- Resume the schedulers on all nodes:
-
Go to System Maintenance > System Overview > Job Scheduling, click on the menu icon on the top left, and then select the Resume Schedulers on All Nodes option.
- Unlock the application:
- Go to System Maintenance > System Overview > System Locking, and then click on the Unlock Application button.
- For restartable extensions: in addition to the steps described above, shut down the extension before deployment and restart it afterwards.
- For permanent extensions: use Method 1 above (Shutdown and Restart), as permanent extensions cannot be stopped at runtime.