Business Data Storage (BDS)
Introduction to the Business Data Storage
The Business Data Storage allows storing and retrieving business data gathered through FNZ Studio Processes to a Relational Database.
The Business Data Storage replaces and enhances the functionality previously provided by the Data Store Extension with improved performance, stability and security, as well as enhanced user experience through a user interface which is now fully integrated into FNZ Studio Studio Composition. The Business Data Storage is delivered as an extension.
Following is a list of the main features of the Business Data Storage with links to the articles providing complete information:
- It provides a thorough user interface in FNZ Studio Studio Composition (Data & Integration > Business Data Storage) that allows you to select, synchronize, and configure Data Classes, as well as check the database content. Moreover, it provides three sensors that allow identifying those situations which require correction. For more information, see the Studio Modules and the Sensors sections.
- It synchronizes a set of selected Data Classes to a Relational Database. Therefore, it transforms FNZ Studio Data Class model into a Database model by creating Database tables for each Data Class. For more information, see the Database Model Synchronization article.
- It provides Script Functions to Save, Load and Delete Data Class instances from the generated Database tables. This allows managing the persistence of Data Class instances to the Database model produced by the Synchronization algorithm. For more information, see the Operations article.
- It provides a set of functions that can be used inside FNZ Studio Solutions. For more information, see the Script Functions article.
Finally, refer to the following recipes for further information on:
- Setting Up Database Users for the Business Data Storage
- Securing and Auditing the Data Handled by the Business Data Storage
Setup and Pre-Requisites
The Business Data Storage requires the BusinessDataStroage Extension to be installed in order to work properly and a compatible DBMS. Consider that PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server.
To set up a Database user to be used by the Business Data Storage, you need to perform the following steps directly on the Database (outside of Appway):
- Create a new Database user.
- Give to the user the necessary grants for the Business Data Storage.
The procedure differs a bit for each DBMS. Here are the deailed steps for each of the supported ones.
Database User Setup for PostgreSQL Data Sources
Follow these steps:
-
Create a new database user:
CopyCREATE USER data_team_user WITH
LOGIN
NOSUPERUSER
NOCREATEDB
NOCREATEROLE
NOINHERIT
NOREPLICATION
CONNECTION LIMIT -1
PASSWORD 'data_team_pwd';
CREATE SCHEMA data_team_schema
AUTHORIZATION postgres;where postgres is the admin user considered.
Note that the user (and schema) name used in the script above is just an example, any user (and schema) name allowed by PostgreSQL can be used.
-
Set BDS grants:
CopyGRANT CREATE, USAGE ON SCHEMA data_team_schema TO data_team_user;
GRANT USAGE ON ALL SEQUENCES IN SCHEMA data_team_schema to data_team_user;These also include grants needed for the username logging feature (see Securing and Auditing the Data Handled by the Business Data Storage ). For more information see: Postgre.
Note that a quoted user is supported by the BDS.
Database user Setup for Oracle Data Sources
Follow these steps:
-
Create a new database user:
CopyALTER SESSION SET "_ORACLE_SCRIPT" = true;
CREATE USER data_team_user IDENTIFIED BY data_team_pwd
ALTER USER data_team_user QUOTA unlimited ON USERS;Note that:
- The user name has to be the same as the schema name defined in the Data Source.
- The user name used in the script above is just an example, any user name allowed by Oracle can be used.
- A quoted user name is not supported by the BDS.
-
Set BDS grants:
CopyGRANT CREATE SESSION TO data_team_user;
GRANT CREATE TABLE TO data_team_user;
GRANT CREATE SEQUENCE TO data_team_user; -
Set username logging related grants. These grants are needed for the username logging feature (see the Securing and Auditing the Data Handled by the Business Data Storage recipe). For more information see: Oracle.
CopyGRANT CREATE ANY CONTEXT to data_team_user;
GRANT EXECUTE ON SYS.DBMS_SESSION TO data_team_user;
GRANT CREATE PROCEDURE TO data_team_user;
Database user Setup for Ms SQL Server Data Sources
Follow these steps:
-
Create a new database user:
CopyCREATE DATABASE DataTeamDatabase
USE DataTeamDatabase
CREATE LOGIN DataTeamUser
WITH PASSWORD = 'YourStrong!Passw0rd',
DEFAULT_DATABASE = DataTeamDatabase;
CREATE SCHEMA DataTeamSchema
CREATE USER DataTeamUser FOR LOGIN DataTeamUser WITH DEFAULT_SCHEMA = DataTeamSchemaNote that the user name used in the script above is an example: any user name allowed by Ms SQL Server can be used. If a quoted user name is used, the quotes must also be used in the Appway Data Source configuration. A quoted user is supported by the BDS.
-
Set BDS grants:
CopyGRANT CONNECT TO DataTeamUser
ALTER ROLE db_datareader add member DataTeamUser
ALTER ROLE db_datawriter add member DataTeamUser
ALTER ROLE db_ddladmin add member DataTeamUser
USE MASTER
GRANT VIEW ANY DEFINITION TO DataTeamUserFor more information, see the related documentation.
Business Data Storage User Interface
If the Business Data Storage is installed, the Business Data Storage submodule grouping is displayed in the Data & Integration module of FNZ Studio Composition.
The three following submodules are then available:
- Configuration
- Stored Data Classes
- Database Content
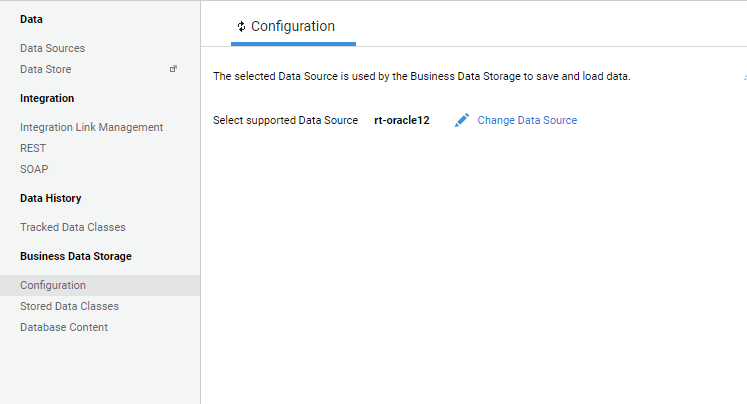
Configuration
On this screen, the Studio user can select the Data Source to be used. The Business Data Storage saves and loads the corresponding data.
- Choose the Data Source to be used from the Select supported Data Source dropdown list.
Consider the following information:
2. Once the Data Source selection has been saved, it is possible to edit it by clicking on the Change Data Source button. However, when changing from Data Source A to Data Source B, consider the following information:
- Only Data Sources of supported vendors (PostgreSQL, Oracle, and Microsoft SQL Server) are shown in the dropdown list. The vendor is specified in the Database Vendor dropdown list of the Data Source configuration dialog (Data&Integration > Data > Data Sources > Add [JDBC/JNDI] Data Source).
- It is mandatory to specify a Schema Pattern for the Data Source used by BDS.
- This change affects Data Class synchronization. Data Classes may need to be re-synced.
- The data saved in Data Source A are no longer accessible (although they are not deleted).
- The data already contained in Data Source B are visible to the Business Data Storage.
- After changing from one Database vendor to another (e.g. from Oracle to PostgreSQL), it is recommended to call the function BDSCleanupAndSyncAllDataClasses to regenerate the table and column names compatible with the new Database.
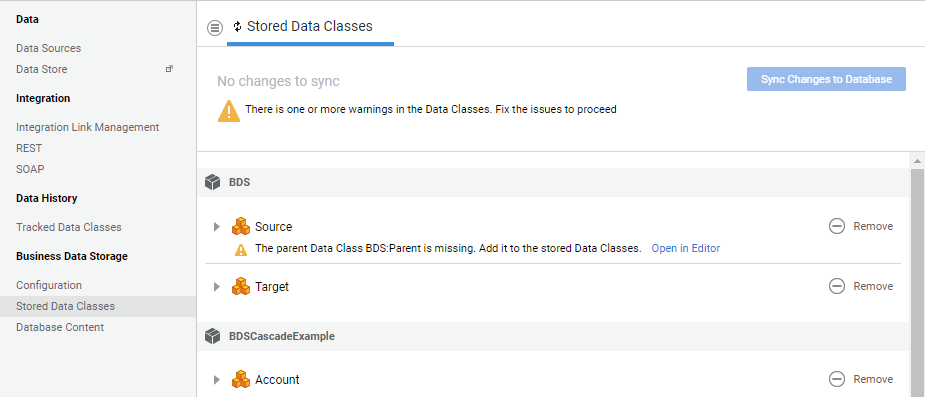
Stored Data Classes
On this screen, the Studio user can perform the following actions:
- Configure the Data Classes to be stored to the Database and the cascade modes on their properties.
- Synchronize the Database according to the selected Data Classes.
- Verify whether the Data Classes are currently synced to the Database.
- Verify any possible issues in the Data Model, e.g. unsupported primitive types that prevent the Data Classes from being synced to the Database (see the Verification Algorithm and Configuration Validation Algorithm sections in the Database Model Synchronization article).
Note the following information on Data Classes:
- Data Classes contained in the Base Package cannot be stored using the Business Data Storage. Such Data Classes, in fact, are not shown in the Business Object Selector at the bottom of the page.
- Data Class replacements are not supported when storing Data Classes. See the Packages documentation.
To perform these actions, follow this workflow:
-
If no Data Classes were previously added, click on the Select a Data Class... Business Object selector at the bottom of the page, click on the desired Data Class, and then click on the Add Data Class button.
-
At this point, two types of information can be displayed both at the Data Class level and at the single property level. To display it, open the Data Class interline:
- Warning (yellow icon): a warning is an issue that prevents the changes from being synced to the Database, e.g. the Data Class contains a property whose type is not supported. To solve these warnings, click on the Open in Editor button to open the Data Class Editor in a new tab and make the necessary edits.
- Out-of-sync (grey icon): Data Classes are not (yet) synced to the Database, as changes have not been saved. This is the standard case, as Data Classes are synced to the Database only after saving. The full list of out-of-sync situations for a stored Data Class can be found in the Recap of DB out-of-sync situations and corresponding actions taken by the Sync algorithm section in the Database Model Synchronization article.
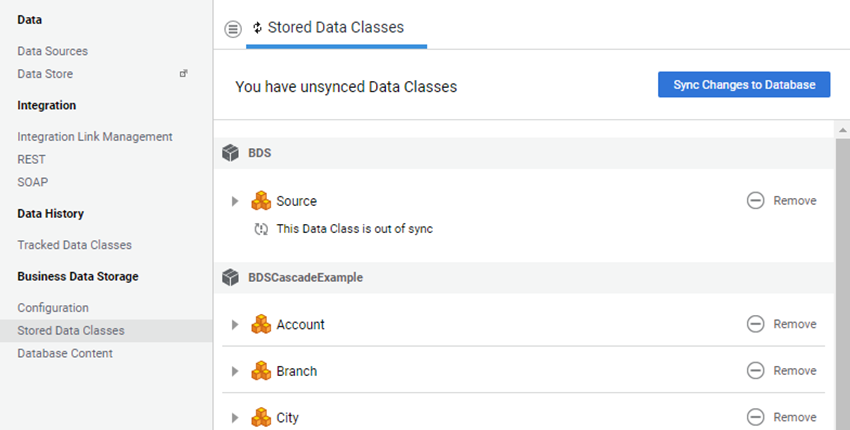
-
If necessary, open the Data Class interline and set the cascade mode for each property of each added Data Class from the related dropdown list. The dropdown list is only available for those properties whose type is a Data Class stored with the BDS. The default cascade mode is Load (for more information, see the Operations article).
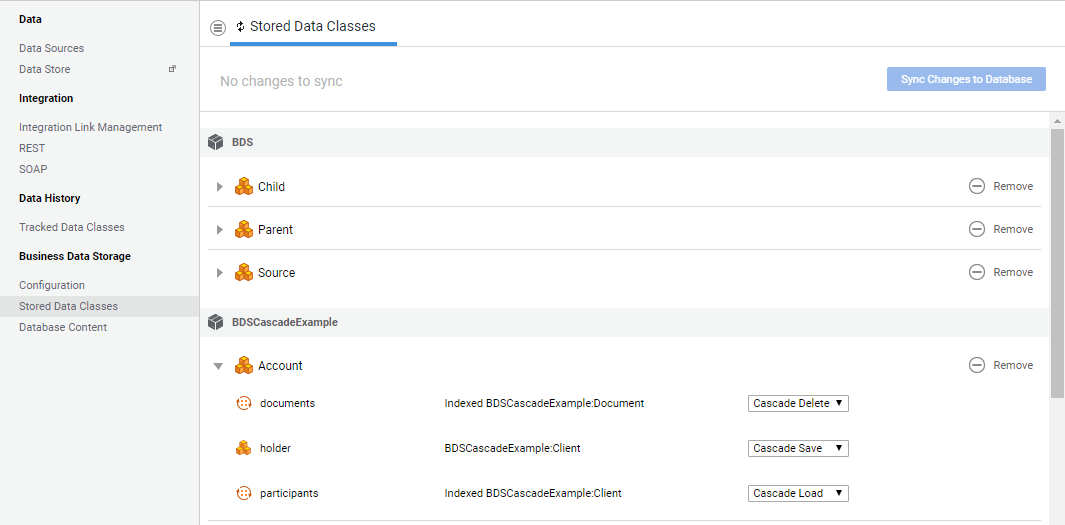
-
Once all warnings are solved and the desired cascade modes configured, click on the Sync Changes to Database button. This creates the Database tables and columns according to the logic described in the Database Model Synchronization article.
Note that the synchronization process might take some time to complete. 5. If all Data Classes are synced, a positive feedback message is displayed.
Otherwise, there are two possible scenarios:
- None of the Data Classes could be synced to the Database. A global error message is displayed and it is possible to try syncing again with the Sync Changes to Database button.
- Some Data Classes could not be synced to the Database. In this case, the error is displayed with a red icon on each failed Data Class. It is possible to try syncing again with the Sync Changes to Database button (see image below).
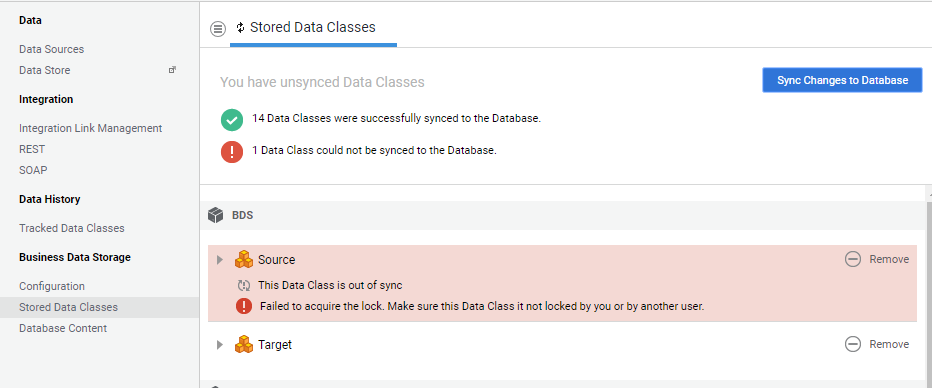
Adding, Moving and Changing Data Classes
To add more Data Classes to be stored to the Database at a later point, you can repeat the steps described in the previous section.
You can also remove a previously stored Data Class. This operation does not remove any data or Database table, it only prevents saving further data for the removed Data Class in the future. Note that if a removed Data Class is added back at a later point, it is associated with a new table.
Finally, every time a stored Data Classes is changed (e.g. a property is added or removed, a type is changed, the inheritance settings are changed and so on), you need to go back to the Stored Data Classes screen, verify that no warnings are present and sync again with the Sync Changes to Database button. The out-of-sync information is displayed on the screen accordingly.
Database Content
On this screen, the user can check the current content of the Database (tables, columns, number of entries for each table).
For each Package where at least one Data Class is stored, a table with the list of Database tables is displayed. The tables listed here are either Main tables, Bridge tables or Collection tables. For each table, the type and number of entries is shown.
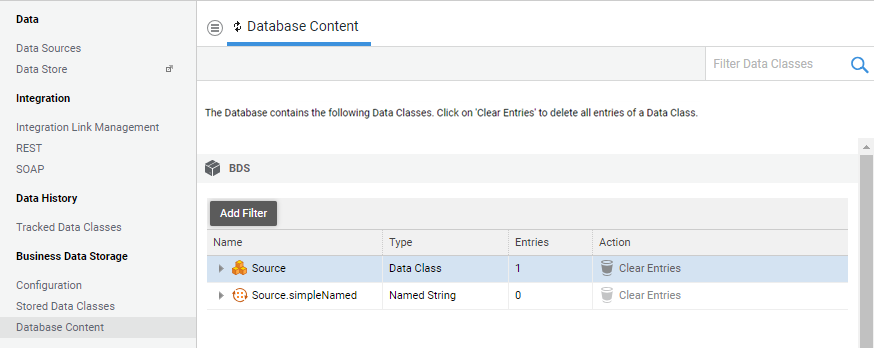
By opening the interline of each table, it is also possible to browse technical information about the Database objects:
- For Bridge and Collection tables, the Database Table Name is shown.
- For Main tables, in addition to the table name, also the details for each property of the related Data Class (table/column name) are listed. This information may be used to write any direct SQL query on the Database, if necessary.
Note: It is not possible to execute SQL queries from this screen.
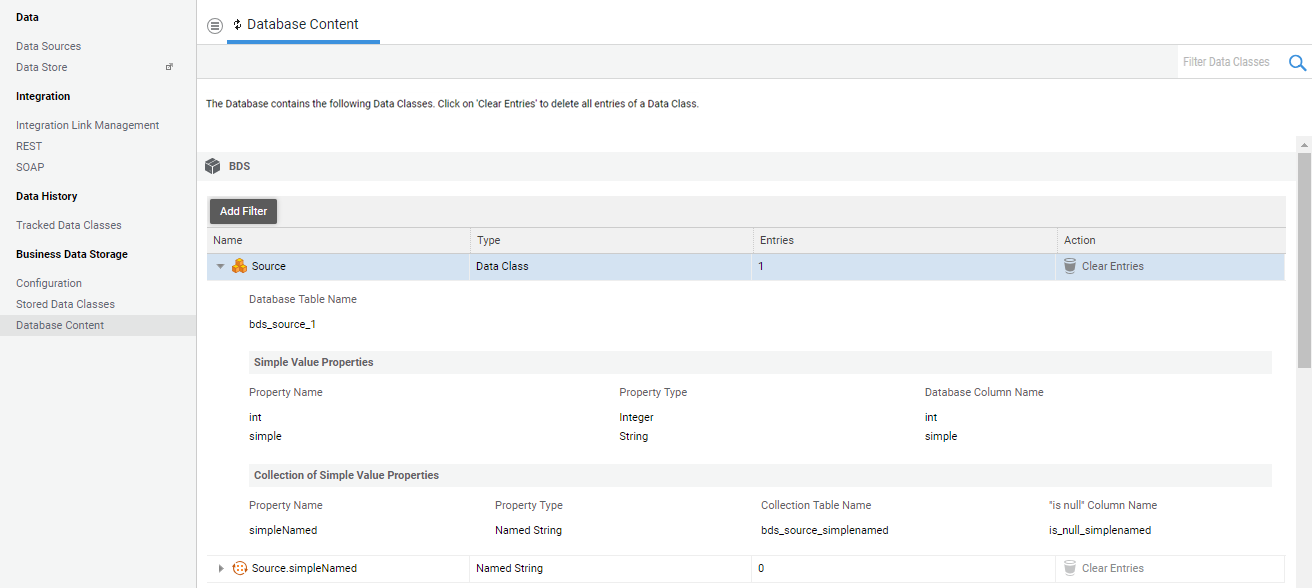
From this screen, it is also possible to perform two actions:
- Clear Entries: deletes all rows from the selected Database table. The button is is displayed on the table row. It is disabled if there are no entries.
- Clear All Entries (from the Database Content menu icon): deletes all rows from all BDS Database tables. This button is displayed when clicking on the Menu icon on the upper-right corner.
Business Data Storage Sensors
The Business Data Storage provides three sensors that allow the developer to easily identify situations which require (immediate) correction:
- Business Data Storage Data Source Configuration
- Business Data Storage Sync Status
- Business Data Storage Configuration Conflicts
- Business Data Storage Duplicated IDs Sensor
Business Data Storage Data Source Configuration Sensor
This sensor is able to identify and report issues in the Data Source configuration for the BDS. The problematic situations reported by this sensor are:
- no Data Source is selected for the BDS, but at least one Data Class is configured to be stored.
- the Data Source selected for the BDS does not exist.
- the Database vendor of the selected Data Source is not supported by the BDS.
- the Database vendor of the Data Source selected for the BDS is not correct (the selected vendor does not match the one returned by the Database driver).
- no Schema Pattern is specified for the Data Source selected for the BDS.
- the Schema Pattern specified for the Data Source selected for the BDS does not exist.
These checks are executed every 10 minutes.
If one of these issues is encountered, the user is guided to the Data & Integration > Business Data Storage > Configuration submodule to verify the selected Data Source:
- From the sensor banner, click on the Open System Health button to be redirected to the System Maintenance > Health submodule.
- Right-click on the sensor and select the Open Configuration option.
Business Data Storage Sync Status Sensor
This sensor is able to identify and report out-of-sync situations where the Database model is not aligned with the FNZ Studio Data Model. For example, a new SV property has been added to a stored Data Class, but the corresponding column has not been added yet to the main table.
The full list of out-of-sync situations for a stored Data Class can be found in the Recap of DB out-of-sync situations and corresponding actions taken by the Sync algorithm section in the Database Model Synchronization article.
The sensor lists the Data Classes where at least one out-of-sync situation is found. If there is at least one out-of-sync stored Data Class, the user is guided to the Data & Integration > Business Data Storage > Stored Data Classes submodule.
This check is executed every 30 minutes.
- From the sensor banner, you are redirected to the System Maintenance > Health submodule.
- Right-click on the sensor and select the Open Stored Data Classes option.
- Detailed information on the out-of-sync situation is displayed and you can sync all stored Data Classes again.
Business Data Storage Configuration Conflicts Sensor
This sensor is able to identify and report conflicts in the configuration of stored Data Classes, for example when more than one Data Class corresponds to the same main table.
The detailed list of possible conflicts and resolution strategies can be found in the Configuration Validation Algorithmin the the Database Model Synchronization article.
The sensor lists the Data Classes where at least one configuration conflict is found. If there is at least one stored Data Class with conflicts, the user is guided to the Data & Integration > Business Data Storage > Stored Data Classes submodule.
- From the sensor banner, you are redirected to the System Maintenance > Health submodule.
- Right-click on the sensor and select the Open Stored Data Classes option.
- Detailed information on the conflict is displayed and you can take appropriate actions for its resolution.
This check is executed every 35 minutes.
Business Data Storage Duplicated IDs Sensor
This sensor is able to identify and report any duplicated persistence IDs found in BDS tables (more than one Data Class instances with the same persistence ID).
If the sensor reports such an issue, Save, Load and Delete operations fail due to the inconsistent state of data.
The sensor lists the tables where the duplication occurs. If there is at least one duplicated persistence ID, the user is guided to the Data & Integration > Business Data Storage > Database Content submodule.
- From the sensor banner, you are redirected to the System Maintenance > Health submodule.
- Right-click on the sensor and select the Open Database Content option.
- Detailed information on the affected tables and their content is shown and you can take appropriate actions for resolution.
This check is executed daily at 3 AM and right after the BDS Extension is started.
Business Data Storage: Script Functions
The BusinessDataStorage Extension also brings to FNZ Studio Script Functions allowing to perform a variety of operations. Check out the BDS Script Function article to get more details
Business Data Storage: Technical Insights
The Business Data Storage manages automatically the interaction with the database, leaving to the developer just the effort to setup the persistence propertly and to write the code to perform the desired operations, however, behind this automatic database interaction there are a lot of technical aspects that we may want to deepen. The following articles provide more details on some techincal aspects:
- BDS Operations - which provides more details on Save, Load and Delete operations and Cascading
- BDS Database Model Synchronization - which provides more details on the Synchronization between Data Classes and DB.
- BDS Securing and Auditing - which tackles security aspects in depth.
Other Resources
You can also browse additional resources around the Business Data Storage by browsing the following pages: