Secrets Management Framework
Introduction
Secrets Management makes it easy to securely store and access secrets in FNZ Studio.
All of these secrets are centralized in FNZ Studio Composition under System Configuration > Passwords, Keys & Certificates, which allows storing secrets such as:
- Passwords and secrets
- Public-Private Key Pairs (used for mTLS, signing, and so on)
Moreover, it allows storing:
-
Trusted Certificates (third-party certificates trusted by FNZ Studio)
-
Symmetric Keys
Note: To access this module, the Encryption Studio Permission must be enabled.
Secret Manager Framework
As mentioned above, FNZ Studio comes with an embedded secrets manager by default. This can be used to store secrets in a secure way if no other external system is installed. These secrets are marked as EmbeddedSecretsManager in the Passwords tab (Secrets Manager column).
In addition, FNZ Studio also supports the integration with external secret managers to store passwords and key pairs (also for permanent extensions). Currently, AWS Secrets Manager is supported. These secrets are marked as AWSSecretsManager in the Passwords tab (Secrets Manager column).
Extensions
External secret management is provided through extensions that can be installed in FNZ Studio. These are stored in the Secrets Manager Extensions section under System Configuration > Extensions (see the Managing Extension article for more information on extensions). As a first step, therefore, you need to make sure the extension is installed.
Secret management extensions are started before any other permanent or non-permanent extensions, so that secrets can be accessed by other extensions. Moreover, they can be started or stopped at runtime. For all these extensions, the com.nm.adapter.IsSecretsManager configuration property set to true in the adapter.cfg file.
Extension properties with sensitive information are stored as an Embedded Secrets Manager by default. Permanent extensions cannot use the Embedded Secrets Manager to store secrets, since they are started before the cluster storage is available. For permanent extensions to store secrets securely, a Secrets Manager Extension must be installed.
Currently, AWS Secrets Manager is enabled through the AWSSecretsManager Extension and operates in read-only mode, meaning that it does not support the ability to create, update or delete secrets.
AWSSecretsManager Extension
The AWSSecretsManager Extension allows managing secrets in the AWS Secret Manager.
Authentication
The AWSSecretsManager Extension uses the AWS Java SDK to connect to AWS. The SDK uses the default AWS credential provider chain to determine the credentials to use. If the extension is running on an EC2 instance, the SDK will use the instance profile credentials. Therefore, there is no need to provide the access key and secret key in the extension configuration.
If the extension is running outside of AWS, the access key and secret key can be provided in the extension configuration using the following properties:
com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.accessKey = The AWS access key.
com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.secretKey = The AWS secret key.
Other Properties You can set the following properties:
com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.region- Specifies the AWS region.com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.read-only- Set it totrue, if the AWS Secret Manager should be read-only. In this case, the extension will not be able to create, update or delete secrets.com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.secret.prefix- Specifies a prefix for the secret names. If the property is set, the extension will prepend the prefix followed by the/separator to the secret name when accessing the secret in AWS Secret Manager.com.nm.extensions.awssecretsmanager.encryptionKeyId- Specifies the encryption key ID to be used when creating a secret. The encryption key ID must be a valid AWS KMS key ID.
Configuration Properties
Moreover, external secret managers need to be enabled through the nm.secrets.managers.active configuration property (System Configuration > Configuration Properties), where you can enter a comma-separated list of secret manager names (e.g., nm.secrets.managers.active = EmbeddedSecretsmanager, AWSSecretsManager). Note that this configuration property can be changed at runtime.
Consider the following info information on multiple secrets managers :
- Retrieving secret - If there are multiple secrets managers enabled for a specific secret, the first one in the list is used to retrieve it. If an alias is present in multiple secrets managers, the value is chosen based on the priority set in the configuration property.
- Storing a secret - When storing a secret, the fist secret manager configured in the property is used.
- Creating a secret - When a secret is created, the first secret manager configured in
nm.secrets.managers.activeis used. - Updating a secret - When a secret is updated, it is updated in the secret manager where it was loaded.
- Deleting a secret - When a secret is deleted, it is only deleted from the secret manager where it was loaded.
During startup, all secrets are loaded into memory and cached. The System Maintenance > System Caches submodule provides a way to view cache statistics and clear the cache and reload the secrets.
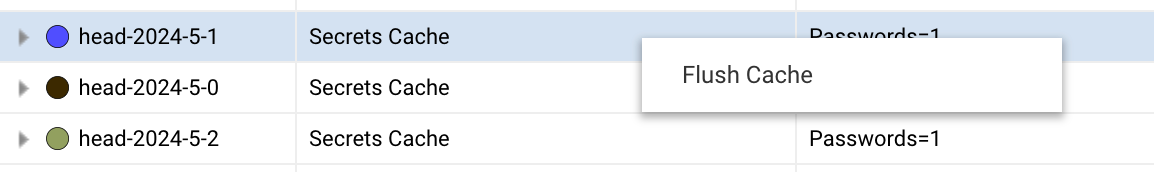
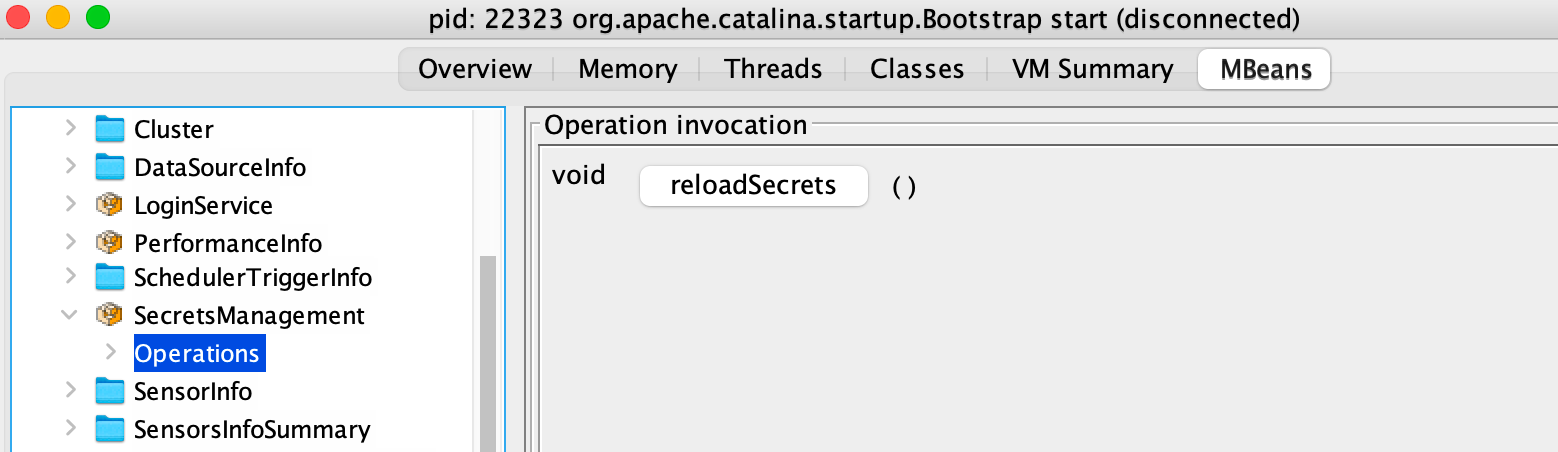
When secrets are changed externally, the cache needs to be reloaded so that secrets become visible. Secrets can also be reloaded through a JMX bean called SecretsManagement.
Tabs
Passwords Tab
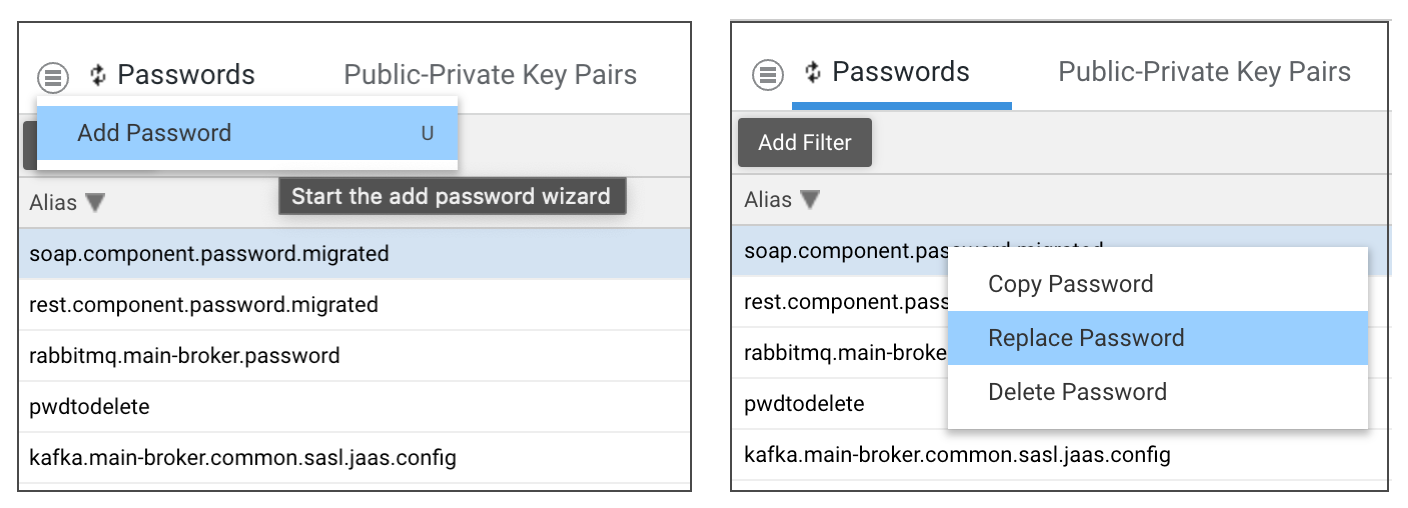
As mentioned above, the Passwords tab contains passwords used by Solutions and extensions to store secrets. Moreover, this tab allows creating, replacing, copying and deleting passwords (if they are not read-only).
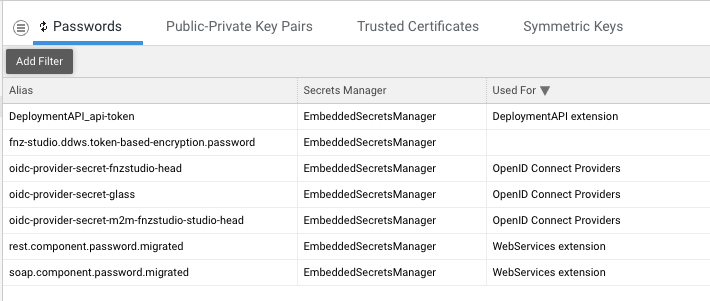
Currently, the page displays the list of passwords aliases along with the Secret Manager being used and the purpose of the password, if this information is accessible.
A user with the right permissions can add, remove, update, and view the value of a password. In this case, the value will be copied to the clipboard.
Note that the same operations can be performed using the following script functions:
-
Auth:HasPassword($passwordAlias) : Boolean -
Auth:RemovePassword($passwordAlias) : Boolean -
Auth:RetrievePassword($passwordAlias) : String -
Auth:StorePassword($passwordAlias, $password) : Nothing
Alias Restrictions
When adding a new password, the alias must comply with the following restrictions:
-
Allowed characters:
-
Lowercase or uppercase letters (a-z, A-Z)
-
Digits (0-9)
-
Others: -, _, =, :, .
-
-
Forbidden characters:
-
Special characters: @, #, $, %, &, *, +, !, ?, and so on
-
Whitespace characters: spaces, tabs, and newlines
-
-
Examples of forbidden aliases:
-
alias@name -
alias name -
alias#name -
alias$name -
alias&name
-
User Personal Passwords
A user's personal password is a specific type of password identified by value User Personal Password in the Used For column.
These passwords are secrets that can be seen and managed only by the user who created them. Currently, these passwords cannot be created in the Passwords tab, rather, it is handled by the Change Tracking feature (Solution Maintenance module).
Public-Private Key Pairs Tab
The Public-Private Key Pairs tab enables the management of Public-Private Key Pairs and their associated certificates.
These keys are used in FNZ Studio for mutual authentication and for signing JSON Web Tokens (JWTs).
The page shows the same information as the Trusted Certificates page explained above, along with the following additional details:
- Key Algorithm: Cryptographic algorithm used for the key pair.
- Key Type: Cryptographic keys used in X.509.
- Key Size: Size of the key.
- Used For: Host intended to use the key for client authentication. Depends on the FNZ Studio configuration property
nm.security.ssl.serverAliasMappings.
As for Trusted Certificates, you can upload, replace, or remove key pairs, view their details, as well as download the public key or certificate.
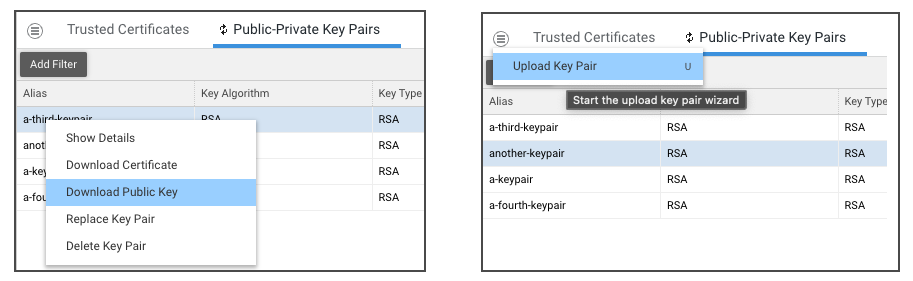
Show Details
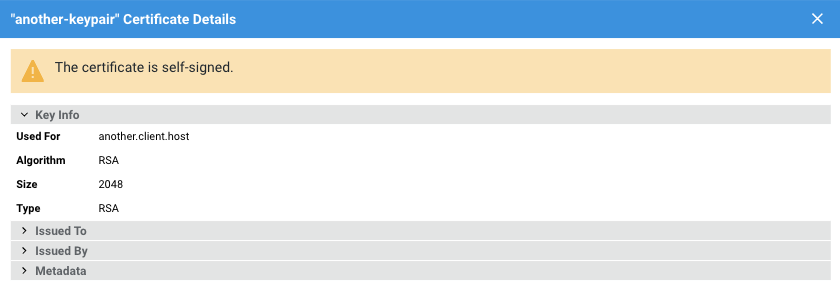
The Show Details action opens a modal window with additional specific information on the selected key pair.
Upload/Replace Key Pair
Similar to the previous module, these actions follow a common two-step guided workflow.
Key pairs are usually protected by a password, but this is not mandatory. During the upload step, the user is prompted to enter the password for the key pair. If the key pair is not password-protected, the password field can be left blank and you can proceed with the action.
Trusted Certificates Tab
The Trusted Certificates tab allows viewing and managing the certificates from the core Trust Store. These certificates are used to enable HTTPS/SSL connections between FNZ Studio as a client and a remote service.
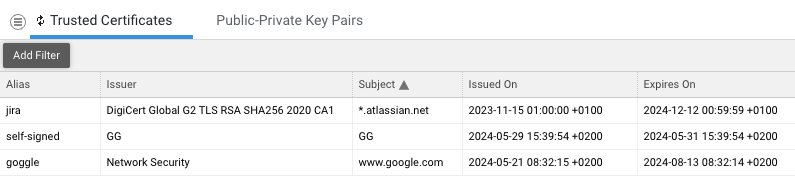
This page displays a list of current certificates, providing the following information for each of them:
- Issuer (Common Name): Entity that issued the certificate.
- Subject (Common Name): Entity to which the certificate was issued.
- Issued On: Date and time at which the certificate was issued.
- Expires On: Date and time at which the certificate is bound to expire.
Additionally, by clicking on the context menu, you can access the following actions for the selected certificate (given the relevant Studio Permissions, as mentioned above):
- Show Details: Opens a modal window showing the certificate details.
- Download Certificate: Downloads the certificate in
.PEMformat. - Replace Certificate: Replaces the certificate associated with an alias.
- Delete Certificate: Delete the certificate (and associated alias).

Furthermore, you can add a new certificate by uploading a .PEM file using the Upload Certificate action from the hamburger menu.
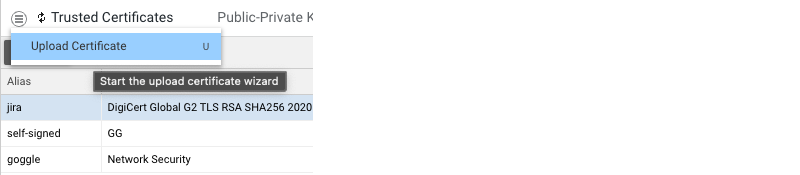
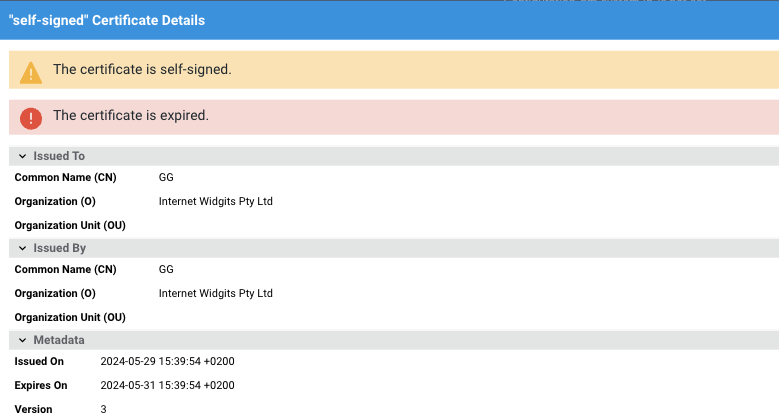
Show Details
This action will open a modal displaying all details of the certificate, including any relevant warnings and errors, if present (note that the screen below shows only part of such details).
Upload/Replace Certificate
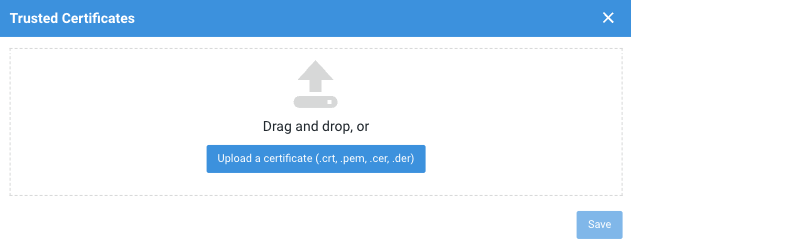
These actions facilitate a two-step guided workflow:
-
Upload certificate: This step involves uploading the certificate that you want to save.
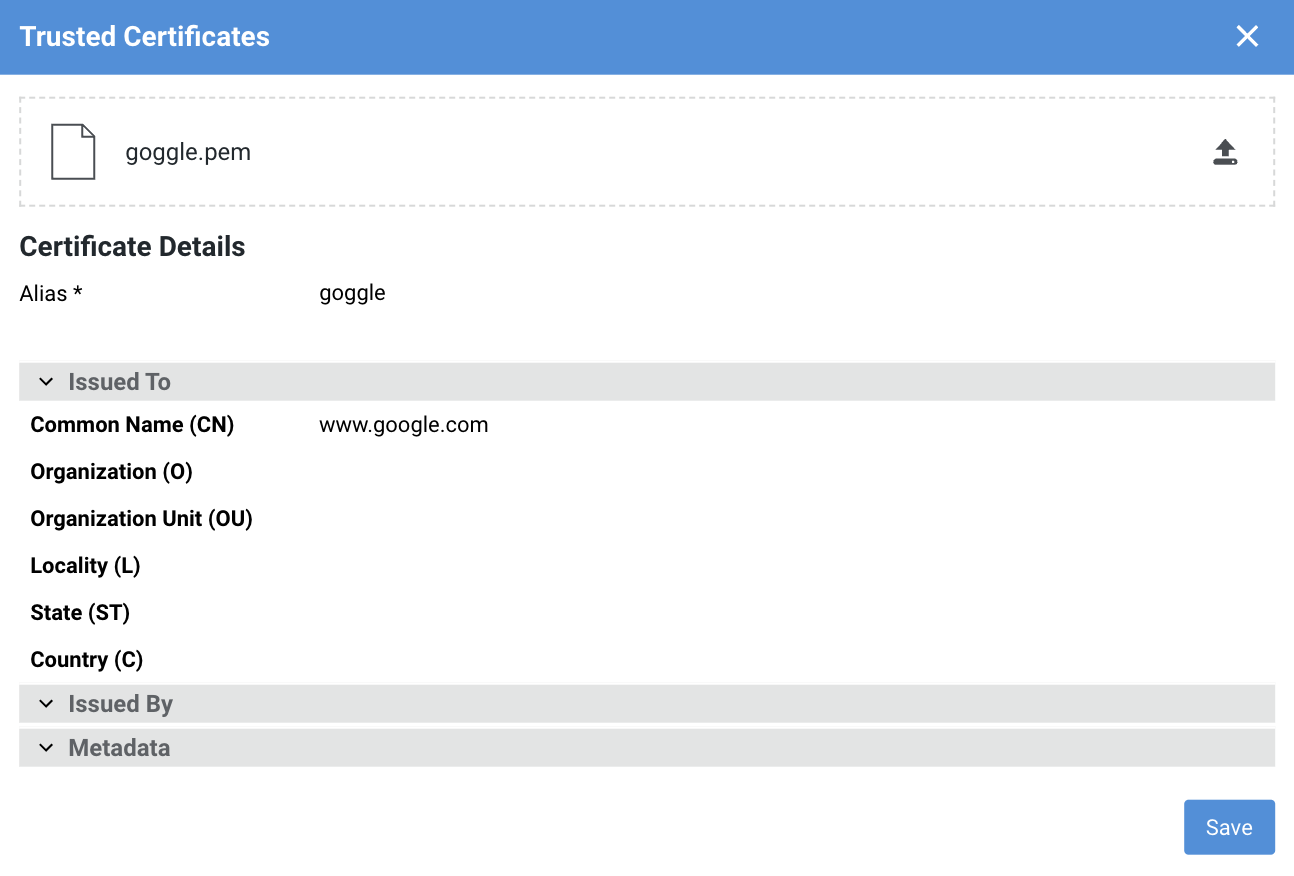
-
Review and Confirm: After upload, a preview of the certificate is displayed. After reviewing the certificate details and, if necessary, providing an alias, you can proceed to confirm the operation.
Symmetric Keys Tab
The Symmetric Keys tab provides a comprehensive overview of the symmetric keys available for cryptographic operations stored in FNZ Studio. Symmetric keys are cryptographic keys used for both for encryption and decryption.
Note that, currently, this tab displays key information in a data table, but it does not support any direct actions.
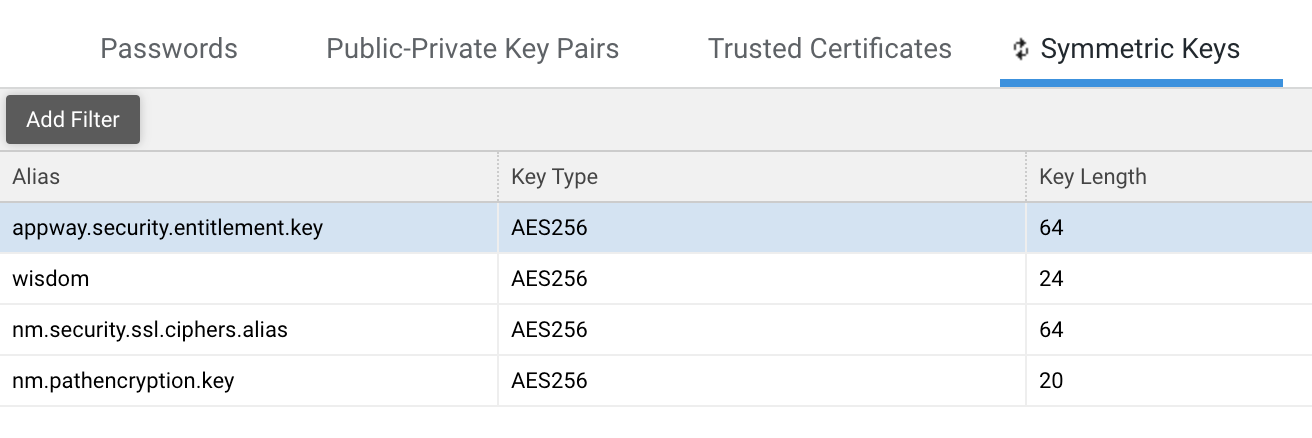
The Symmetric Keys data table shows the following informations :
- Alias: Unique identifier given to each key for easy reference.
- Key Type: Cryptographic algorithm used by the key.
- Key Length: Size of the key (in bits).